Exercise
一. SfM photogrammetry of UAV data in Agisoft Metashape
1. Import photos
为什么不用起飞和降落时候的照片?
The photos from take off and landing have already been removed, so all photos are at the same height level. ==However, the lines are not really parallel, but they are a bit skewed==. Dependent on the field of view of the camera this may cause issues with the overlap and with having enough different viewing angles over the entire scene.
2. Project with UTM projection
Geographic data is often presented in a projected coordinate system, in order to visualize 3D data in two dimensions (on your screen). In this process longitude/latitude is converted to (x,y) coordinates.
Every projection comes with distortions and some projections tend to preserve angle (conformal projections), area (equal-area projections) or distance (equidistant projections). Not a single projection can preserve all three properties. The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) projection averages the degree of distortion over all three properties.
3. Import ground control points
4. Camera Alignment
Which processing steps of camera alignment
- point detection
- matching points
- estimating camera locations
- adjusting camera locations For each picture the software identifies objects, these points are used to match the neighbouring pictures, it selects the identifiable pairs between the neighbouring images and aligns them.
Metashape align all images is this a sequential process
Each time photos are added, which are aligned to the already registered photos
5. Mark ground control points
Show point residuals
there are points which are identified in multiple images and which are thus used as tie-points. (The blue points are used points, used for creating the camera alignment, which also overlapping features of each pair. The grey points are not used for creating the camera alignment.)
However, no all points are shown (at least not ~2000 of them per photo), so they don’t always show up at the same location. Actually that is a bit a vague implementation.
照片没有aligned的原因和解决方法
If some of the photos are not properly aligned there may be too little overlap, or a lack of identifiable features. Changing the quality settings to a higher level may change the number of aligned images, as well as the preselection settings.
6. Build Dense Cloud
7. Build mesh
The other settings include
- tie points and point cloud for source data
- arbitrary (3D)
- height field (2.5D) For a 3D reconstruction you would go for ==arbitrary==, which also allows you to create a mesh on the sides of objects. Also for trees this is the best method. For orthophoto information on the depth is needed and not about the sides of the object, ==height field,== which makes the setting height field sufficient.
8. Build Texture
What can you say about the age of the landslide activation? Is this a very recent landslide or do you think it is already “old”?
The edges are quite ==steep== so this is a fairly recent landslide. If it would have been older the edges would have been less sharp. Also some plant rows are crossing the drainage gullies沟, although not in a straight line
management to improve the stability of the slope
Ploughing parallel to the slope, creating terraces
二. Surface reconstruction of a mixed area with different cameras
P1和X7相机
P1 camera captured more details of the canopies of the trees, compared to X7 that is missing points there. The main difference in the amount of detail between the cameras lies in the capacity of the lens and the GPS system of the device.
All photo’s will be aligned and the pointcloud makes sense. There is enough overlap, so there should be no big issues. Visually you’ll see that it is definitely harder to reconstruct the trees. The pavement, containers, grass etc will look good, but especially the tree crowns will show quite some gaps.
Explain the difference between the different camera’s.
the P1 camera is a pretty good camera, so it can autodetect most of the GCP’s and their codes automatically.
The initial error for the X7 camera will be around 60-70 cm, while for the P1 this is much lower. The use of RTK on the drone is really helpful here, since the starting locations of the pictures are much more accurate (which we could use as a constraint in the model). Personally, I wouldn’t use the X7 without GCP’s when I’m aiming for a very high accuracy, while the P1 in combination with RTK comes pretty close.
Dense Cloud Confidence
The confidence for points on the ground (road) and tops of the emergent trees is highest. These are also the areas which are most stable (==no wind==) or properly covered by multiple images. The areas with lower confidence are probably covered by less photos, lowering the programs confidence indicator.
profile tool
Only when the ground surface is directly visible, but you will have no points on the ground when you are looking at e.g. the maize on the west, trees in the middle, or elephant grass on the east side of the area.
Photogrammetry relies on objects which you can see from ==different directions== with enough contrast to distinguish features
SfM create DSM
(SfM technique as a whole the capabilities of this method to create a DEM of a partially vegetated?) 不能 You will not be able to see what is underneath the vegetation, for sure not from enough different observation angles, to reconstruct the surface. So instead of a DEM you do get a DSM, with all object like vegetation still in it. You would have to remove this and interpolate the terrain height.
三.Generate your own 3D model and evaluate the process.
PPT
Aerial Photography
Benefits
Literally zoom-out, Overview of patterns in landscapes, Better understand context
Platforms
any flying object, including: Aircraft, Helicopter, Balloon, Kite, UAV
Photogrammetry
Science of making reliable measurements by the use of photographs(size, shape, geographic positioning) Reconstructing the geometry of the photographed surface.
Parallax»原理
a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight, and is measured by the angle of inclination between those two lines. 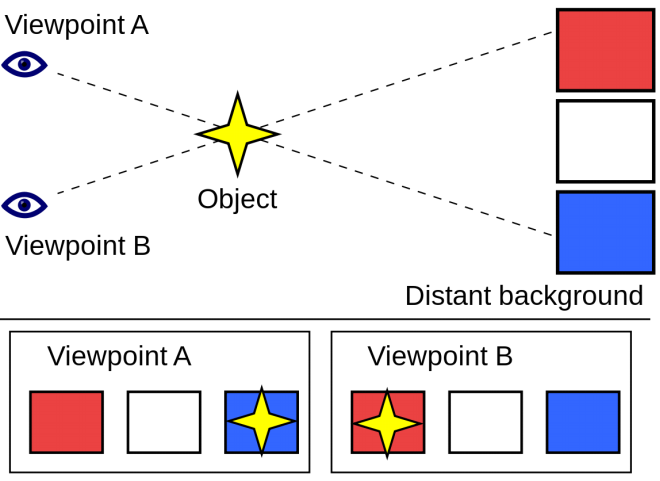
立体视觉»Overlapping Stereophotography
What
- Overlapping photography is needed to determine parallax and stereo/3D viewing»> Forward overlap - ~60% Side overlap - ~20-30%
- Overlapping photos, image pairs»>Same features from different angles in different photos, distorted in a different way
基于:
Inner orientation
- Known camera parameters
- Position of feature in the photo(known degree of distortion) Exterior orientation
- Position and orientation of the camera with respect to the object
- Position and orientation of camera’s to each other
Aerial Photograph航拍图片的问题
- Lens distortion– Distortions toward edge of picture
- Camera tilt – Doesn’t always point straight down
- Altitude variation during flight– Scale varies with elevation
- Earth curvature(地球曲率)– scale 1:10000 – distance > 10 km – dh = 60cm
- Atmospheric distortion– when working at scale of > 1:50000
- Scale varies across photograph due to all previous– Parallax shift历史原因哈哈哈哈
航拍和摄影测量结合
- Use overlap of aerial photos to view photos in stereo
- Correct photos for camera angle and altitude
- ==Parallax shift determines altitude==
Relief displacement
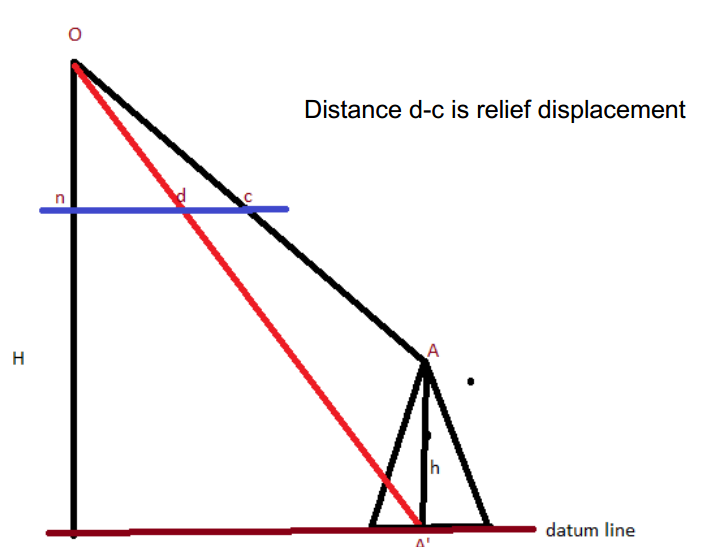
Maps vs. Aerial Photos地图和航拍的比较
Nadir» direct
- Maps: Scale is constant»>No relief displacement
- Photos: Scale varies with tilts and elevation»>Relief displacement
- Orthophoto: aerial photograph with the geometry of a map »>No relief displacement
Stereoscopic Parallax立体视差
- The ==displacement of an object== caused by a change in the point of observation is called parallax.
- Caused by taking photographs of the same object but from ==different points of observation.== ![[43b2a5cd3b79686ec4c4837333aabd8.png]]
Absolute stereoscopic parallax
- PP = Principal point = nadir point of photo (hopefully center)
- CPP = Conjugate principal point = adjacent photo’s PP
- Absolute stereoscopic parallax → the average photo base length = average distance between PP and CPP → related to difference in scale of photos ![[de93a417193ecedbb3a46bdff0b2904.png]]
Differential parallax
Differential parallax - the difference between the stereoscopic parallax at the top and base of the object. ![[469a2cf4d339ae69a57a43de7d857be.png]]
Computing height using stereoscopic parallax
- If we know: Camera orientation, Orientation of the photo in the camera:
- h = (H’) * dP / (P + dP) where h = object height, H’ = flying height, dP = differential parallax, P = average photo base length
Calculating Object Heights
- Object heights can be determined as follows: calculate flight altitude (H’) by multiplying the scale denominator by the focal length of the camera
- ==h = d * H’ / r ==where: h = Object height(要求的), d = length of object from base to top, r = distance from P.P. to top of object , H’= Flying Height above terrain ![[a1dd4a06465717c7d3bdd5d3946f2f2.png]]
Source of distortion扭曲的来源
- Lens distortion
- Camera orientation with respect to the object相机相对于物体
- Camera distance with respect to the object相机相对于物体的距离用 Camera Calibration(相机标定)来修正
Structure-from-Motion(SfM) photogrammetry
Automated surface reconstruction
- Automated feature detection
- Automated estimation of internal camera parameters (distortion)
- Automated estimation of external camera parameters (position and orientation)
- Automated 3D reconstruction of the object or landscape
Input:
- Very large collection of photos with high degree of overlap
- GPS information in EXIF metadata of imagery already geo references the surface reconstruction.
Output
- 3D point cloud
- Mesh → Digital Surface Model网格
- Texture → Orthorectified mosaic纹理
SfM Objective function:
minimize reprojection error
- 旋转平移:Given point x and rotation and translation R, t
- 最小化SR:Minimize sum of squared reprojection errors g 但Minimizing g is difficult:
- g is non-linear due to rotations, perspective division
- lots of parameters: 3 for each 3D point, 6 for each camera
- difficult to initialize Many techniques use non-linear least-squares (NLLS) optimization (bundle adjustment)用一些非线性技术高级一点
SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) Detector and Descriptor尺度不变特征变换
Image content is transformed into local feature coordinates that are invariant to translation, rotation, scale, and other imaging parameters
(Uses for SIFT)Feature points are used also for:
- Image alignment (homography, fundamental matrix)
- 3D reconstruction (e.g. Photo Tourism)
- Motion tracking
- Object recognition
- Indexing and database retrieval
- Robot navigation
SfM photogrammetry in Agisoft Metashape
流程:
- Camera alignment
- Identify manually measured ground targets»Accuracy ground control mark
- Dense point cloud
- Triangulate mesh
- Blend texture on top of the mesh
Export results
- 3D point cloud
- Digital Surface Model
- Orthorectified mosaic -> map geometry!!
- Only then the “real” analysis starts
Requirements可能遇见的问题
- Enough overlap (min 60%)
- Enough photo’s (min 6)重叠
- Distinctive features (many!)特征
- Stable objects during acquisition稳定
- Multiple camera positions多个相机位置
Accuracy
Source of Error & Solution可能遇见的问题
- Lens Distortions (or properties)»Calibrate camera
- Positions Estimation (XYZ) » RTK GPS attached to camera and Use Ground control points and scale bars (for UAV measured with RTK)
- Camera orientation (roll, pitch, yaw) IMU? But this is technically challenging…
- Overlap Proper flight/image acquisition planning»Stable image features Some objects just don’t work…(e.g. water, moving objects)
- Reconstructing very complex structures» Some objects just don’t work…(don’t expect miracles, they don’t happen in photogrammetry)
文档信息
- 本文作者:Xinyi He
- 本文链接:https://buliangzhang24.github.io/2024/01/18/Advanced-Earth-Observation-3.Photogrammetry/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)
