Exercise 4
Why UAV thermal imaging can monitor vegetation stress?
It sensitivity to disruptions in stomatal conductance
Stage 1: Data exploration and emissivity correction
Highest temperature and lowest(最高温最亮)
- Ground control points deployed to aid with the survey have the highest temperature. Artificial materials tend to be good absorbers, meaning they heat up quicker than natural surfaces.
- Areas with bare soil also have very high temperature values – soils have low relatively thermal inertia, warming up quickly during daytime.
- Vegetated areas have lowest temperatures in the image. This is because plants actively lower their temperature through transpiration.
Surface temperature
irrigated field » low temperature non-irrigated field » high temperature bare soil has low thermal inertia»heats up rapidly during the day Water has high thermal inertia» remain stable temperature during the day so, water is cooler than bare soil.
求 minimum and maximum emissivity value
ɛ(λ) + ρ(λ) + τ(λ) = 1
Separate vegetated areas from bare soil
NDVI thresholding, unsupervised/supervised classification, image segmentation.
After emissivity correction
Emissivity correction will increase recorded temperature values of both vegetation canopies and soil. 变化的裸土的温度差比冠层变化的差异大The impact of the correction will be more evident for soil (i.e. larger change in the retrieved temperatures)because of the lower emissivity value being used.
原因: Since the average radiant temperature of soil is already higher than that of canopy, the correction will increase the temperature difference between the two.
Stage 2: Investigating Plant Stress with Thermal Imagery
CWSI
- Twet»healthy, fully transpiring plant» potential transpiration rate» maximum amount of water that a given plant could release into the atmosphere if it had unlimited access to water
- Tdry»stressed, non-transpiring plant » actual transpiration rates» the actual transpiration rate is a measure of how much water the plant is actually releasing ![[865c45e870191d12600bc14b2ce7911.png]]
Different methods for calculation of CWSI(计算方法)
- theoretical using surface energy balance equation
- empirical using field measurements to establish a relationship between canopy-to-air temperature difference and vapor pressure deficit
- image-based that establishes the baselines based only on the canopy temperature readings(in practical)
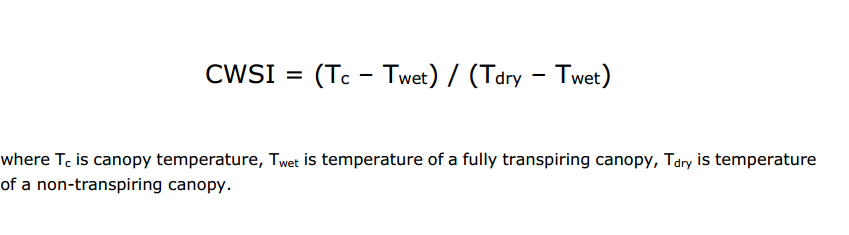
CWSI = 0: no water stress CWSI = 1: severe drought(Tc equals to Tdry)
Distribution of canopy temperature
![[3139caf8433dd005e2b5a61831ec7cd.png]]
- The red baseline is not suitable, as it includes the outliers.
- 最好的The blue baseline cuts the outliers in the minimum and the outliers in the maximum, assuming that based on the NDVI division there might be still values left for the bare soil.
- The green baseline selects the temperature for healthy vegetation, removing the stressed vegetation.
CWSI值越高越接近1
water-stressed and the more stress plants are experiencing
气温变化同时irrigated
Do you think we have violated the assumptions for CWSI calculation and therefore cannot compare index values from these two days?
CWSI的假设是
The assumption for the CWSI calculation that there is a value for healthy vegetation and a value for stressed vegetation in one dataset
Canopy-to-air temperature difference(Tc-Ta)
- (canopy temperature [Tc] - air temperature [Ta])
- is another thermal index used as an indicator of plant water status. It measures deviation of plant canopy temperature from the ambient temperature, providing some normalisation.
- However, it is ==still sensitive== to other ==environmental factors. ==
Bonus: comparison against spectral vegetation indices
Which index offers best separation between the two irrigation treatments?(CWSI NDVI GNDVI, NDRE)
Based on the separability of boxplots, CWSI gives the best separation between the two treatments.
Do you think there would be any value in using a ==combination of thermal and spectral indices== for inspecting water stress? Why/why not?
All computed vegetation indices offer some degree of separation between the two treatments. Scatter plots reveal that these are not closely correlated with CWSI, which means they can potentially provide us with complementary diagnostic information to evaluate vegetation condition. Therefore, using CWSI together with one of the vegetation indices could provide added value and would be worth of further investigation. In this case, it could be done with e.g. linear discriminant analysis that would suggest combining CWSI and GNDVI.
PPT
Temperature and its Application
Climatology, Hydrology, Fire detection, Volcano monitoring
Main Limiting Factor
Poor spatial resolution 但是小型的sensor 提供了新的可能(Miniaturised thermal sensor)
Questions
- Thermal sensor detect的是什么»emitted radiation
- region: 8-14um
- best emitter of radiation: Blackbody
PART 1 - THEORY:
- 什么会影响材料/表面的温度测量?
- 如何从热测量中获得表面的绝对表面温度?
- 什么因素影响热波长辐射与绝对温度之间的关系?
Influence on TIR measurements
![[27abc1a6e8aee6d1dc92b5c71261151.png]]
- 热容量(c)是材料储存热量的能力。
- 导热系数(κ)是衡量热量通过材料的速率。
- 热惯量(TI = (κρc)1/2)*是测量材料对温度变化的阻力。 问题: Pre-dawn»relative temperature B
Emissivity 辐射率
Concept:
Emissivity (ε) = ratio between energy emitted by an object and a blackbody of the same temperature (range of 0 to 1)
Terrestrial surfaces do not act as true blackbodies, emitting only a percentage of the radiance incident on them.
与Reflectance之间的关系
Kirchoff’s radiation law: ==reflectance + emissivity + transmissivity= 1== 问题: B higher emissivity »brighter
Emissivity Correction
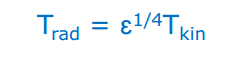 K= 摄氏度+273.15 where Trad is radiant temperature. Tkin is kinetic temperature, ɛ is surface emissivity for the given spectral range.
K= 摄氏度+273.15 where Trad is radiant temperature. Tkin is kinetic temperature, ɛ is surface emissivity for the given spectral range.
Emissivity Value depends on
- material properties– e.g. “darker” objects usually better absorbers and emitters
- surface roughness – rougher surface (relative to the wavelength) = more absorption and re-emission of energy
- moisture content – higher moisture = greater emission
- spatial resolution – e.g. a single leaf has different emissivity to a plant canopy
- viewing geometry
Spectral Emissivity
wavelength must be specific. Emissivity is expressed as a function of wavelength, otherwise known as spectral emissivity
Land surface temperature(LST)地表温度
- Land surface temperature (LST) retrieval from remote sensing imagery requires an atmospheric correction and emissivity correction. 从遥感影像反演地表温度需要进行大气校正和发射率校正。
- 流程: At-sensor data->(radiometric calibration)thermal brightness temperature->(atmospheric correction)->radiant temperature->(emissivity correction)-> Land surface temperature
Problem - have to solve the
coupling between:
- LST and downwelling atmospheric radiance
- LST and surface emissivity
Land Surface Temperature retrieval获取方法
Algorithms depend mainly on the sensor’s spectral characteristics:
- Single-channel (1 band) • Estimate LST by solving the radiative transfer equation (Required inputs: emissivity, atmospheric parameters)
- Split-window (≥2 bands) • Empirically correct the atmospheric effects using the differential atmospheric absorption of adjacent bands(Required inputs: emissivity)
- Multi-angle (1 band & 2 angles) • Differential atmospheric absorption of different viewing paths used to empirically correct the atmospheric effects.(Required inputs: emissivity)
- Temperature emissivity separation (TES, ≥3 bands) • Simultaneously retrieve LST and emissivity»Makes use of the empirical relation between the range of observed emissivities and their minimum value
- Other: day & night image combinations, empirical line method…
Emissivity determination 辐射率的测定
Emissivity value can be estimated utilizing
- land cover classes
- vegetation indices/fractional vegetation cover
PART 2 - APPLICATIONS:
- 如何在环境监测中使用摄像机或扫描仪进行热测量?
- 在应用环境中利用热数据需要哪些处理步骤?
Sea surface temperature(global)
Important to global change studies.
- Emissivity of water = 0.98, therefore accurate (±0.5°C) estimation of absolute temperature possible from TIR radiance.
- Requires atmospheric correction and frequent calibration against surface temperature observations (e.g. buoys / ships) to account for influence of atmospheric aerosols.
Uses:
Identifying currents, Coral reef bleaching, Fish and wildlife habitat, Source of heat at the sea / air boundary (heat exchange)
NOAA Coral bleaching virtual station program
Predicts likelihood of damage to coral sites from high SST. Based on AVHRR measurements.
Urban microclimate城市小气候
- Low albedo(darker surfaces)
- Low thermal inertia of building materials
- Anthropogenic(人类) heat produced by human activities
- Changes to wind speed and patterns(building density and height)
Urban Heat Island(UHI)
dome of high temperatures over urban centers: increase the risk of mortality from excessive heat.过热死亡
TIR remote sensing of UHIs
- ==Emissivity needed==
- good atmospheric correction for comparing images
- ==Conversion of LST to air temperature==
- Comparison to nearby rural areas(Urban Heat Island Intensity)
Geological mapping with TIR
- Differences in ==thermal properties of rocks (spectral emissivity)== can allow them to be distinguished and mapped.
- Geological mapping can be by based on ==emissivity data== (obtained by atmospheric correction and separating from the influence of temperature地质填图可以基于发射率数据(通过大气校正而不受温度影响而获得).
- Alternatively, ==at-sensor radiance== can be used ==directly, using spectral indices.== ASTER-derived TIR lithological indices: Carbonate Index = Band 13 / band 14,Quartz Index = (Band 11 x Band 11) / (Band 10 x Band 12),Mafic Index (silicate content) = Band 12 / Band 13 - Differences in emissivity in different wavelengths can be ==characteristic of certain minerals== (e.g. silicates, sulphate and carbonate). - ==ASTER== - first satellite-based TIR sensor with sufficient spectral (5 bands), spatial (90 m) and radiometric resolution for geological applications.(TIR lithological indices: Carbonate Index…)
Soil moisture and thermal inertia
- Moisture influences surface thermal properties. - ==Thermal inertia== (diurnal temperature variation) can be related to surface (2-4cm depth>> top few cm's of soil layer) ==soil moisture==热惯性(日温度变化)与地表(2-4cm深度)土壤湿度有关。 - Needs high temporal resolution data! because sensitive to soil type, requires bare soil, only sensitive to top few cm’s of soil layer **Bare and Dry Soil Low thermal capacity and Low Conductivity; Water High thermal capacity and High Conductivity** 热容量和导热系数 ### Plant Stress Leaf temperature is primarily determined by the ==rate of transpiration==, responsible for cooling of the leaves. 在压力下:Under stress, ==stomatal closure== 气孔occurs, which helps reduce water losses #### Rate of transpiration 蒸腾速率被这四个因素影响 - Incoming radiation - Relative humidity - Air temperature - Wind speed #### Daily Pattern of Transpiration日变化蒸腾 Stomates respond to light, being open during the day and closed at night ##### Under water stress photosynthesis can be overridden and ==stomates closed down==气孔关闭 for certain parts of the day to ==reduce water loss.==>> found to lead to ==increased leaf and plant temperature.== ##### Under extensive water stress where the plant is unable to rehydrate(补充水分) at night, the ==stomates will remain closed all day.== #### Needs(4 factors)要监测蒸腾要四个
- High spatial resolution(UAVs)
- Optimal Timing(to maximise temperature differences)
- good segmentation of plant canopies
- Have to establish ==the relationship between canopy temperature and transpiration rates or stress levels==. The relationship between leaf temperature and stomatal conductance is affected by ==weather conditions.==
Thermal Stress Indices
- normalize canopy temperature for meteorological conditions.
- CWSI(Crop Water Stress Index)Measure of the ==relative transpiration== rate of a plant. Requires the non-water-stressed baseline and the maximum stressed baseline for calculation. ![[7736a45d9866a43c3df3608953c7707.png]]
Summary
- Thermal sensors ==detect emitted radiation== 探测辐射
- The concept of ==blackbody== ( a hypothetical perfect radiator) is fundamental to get surface temperature from thermal measurements黑体
- The amount emitted ad thermal radiation at a point in time depends on ==kinetic temperature== and ==emissivity== 热辐射量取决于K 温度
- ==Kinetic temperature== of a given surface is determined by the ==surface energy budget== and its ==thermal properties== K温度又取决于T温度
- Thermal properties: thermal capacity, conductivity, inertia 然后T温度又取决于
- Thermal infrared(TIR) data has applications across many disciplines应用广泛
- To get surface temperature ,the remote sensing thermal data must be corrected for atmospheric influences and emissivity effect(==wavelength-specific values==)怎么获得实际LST
- Knowledge of thermal properties of the target surface (3)can help ==interpretation of the thermal signal==, ==selection of appropriate data== (e.g. timing) and ==processing workflows==.
- Multiple days: ==diurnal effects== must be considered during analysis and interpretation. LST values cannot be compared as easily as reflectance values.多日的热图像比较
文档信息
- 本文作者:Xinyi He
- 本文链接:https://buliangzhang24.github.io/2024/01/19/Advanced-Earth-Observation-4.Thermal-infrared-remote-sensing/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)
