Exercise
1. Visualization
直方图的分布类型
- 正态分布(Normal Distribution): 也称为钟形曲线,是一种对称的分布,具有单一的峰值。大多数观测值集中在均值附近。
- 均匀分布(Uniform Distribution): 所有数值具有相同的概率分布,直方图呈现为一个水平线。
- 正偏分布(Positively Skewed Distribution): 也称为右偏分布,具有一个较长的右尾。大多数观测值集中在左侧,而右侧有一些较大的异常值。
- 指数分布(Exponential Distribution): 呈现指数衰减的形状,通常用于描述随机事件的时间间隔。
- 双峰分布(Bimodal Distribution): 具有两个峰值的分布,但不一定非对称。两个峰值可能具有相似或不同的高度。
- 对数正态分布(Log-Normal Distribution): 对数正态分布的直方图在普通尺度上可能呈现非对称形状,但在对数尺度上更接近正态分布。
- 混合分布(Mixture Distribution): 结合两个或更多不同分布的特征,可能导致多个峰值或非对称形状。
Stretch
Compare “Stretch: 100%” (full range of pixel values), “Stretch: 90%” (only the range between the 5th and 95th percentile), and “Stretch 1 σ” (range between mean - 1 std and mean +1 std). 哪个更好地区分了IF和F,heterogeneous 啥的,还有pepper and salt effect
2. HHHV backscatter ratio
HH-HV By subtracting HV value from the HH, the difference between the bimodal peaks is removed, bringing the distributions together. 水是相对均匀的,所以水的标准差很小
3. Analysing and describing class specific backscatter characteristics
Jefferies-Mathuis distance(JMD)
High JMD values between two classes means these two classes are more separatable. And when JMD value close to 0 means that they have similar values, which makes them difficult to distinguish for one another. Euclidean distance
4. Class specific scatter mechanisms
- Water: surface scatter
- Forest: Volume scatter
- Non Forest :The rest of the scattering mechanisms, measured in the HH, have lower intensity in the forest, but higher in the non-forested areas, resulting in higher contrast between these classes.
- Inundated Forest: HH 疯狂double bounce, HV就跟Forest差不多The signal over inundated forest will be reflected perpendicularly from the smooth water surface to the tree trunks and from the tree trunks it would be sent back to the sensor.
L-band 和C-band哪个更适合这个研究forest
L!!! Non-forest is in this study area referring to the mines, which have rougher soil surfaces & second vegetation (grass), forest debris (fallen branches). Rougher surfaces would have more interaction with C-band signal, because L-band signal does not see the individual smaller rocks on the soil surface. Taking that into account, the C-band would have less contrast between the canopies and non-forested areas.
PPT
high backscatter» both VV and VH greener in tropical »more volume purple » high VV, low VH» high surface, low volume ![[27e4f309fb3e9211b0a65021e5cfcc5.png]]
Radar Fundamentals
- all radar system is SAR»Side-looking airborne radar (SLAR)
- incidence angle will change with near range/far range
- VH == HV
- Backscatter often given in 𝜎0(sigma nought» surface) or γ0(gamma nought»stable) in dB scale(small) 不懂回去找 optical vs radar, Side-looking airborne radar, radar geometry, ascending and descending orbits, wavelength, polarisation, Radar measurement, gemetric effects(layover>shadow, foreshortening>weak return) speckle
Scattering mechanisms of forest
==Backscattered== signal mainly results from:
● Volume scattering ● Surface scattering ● Single-bounce scattering ● Double-bounce scattering
==Relative contributions== depend on:
● Surface roughness ● Dielectric properties of the medium
==All of these factors== depend on:
● The radar wavelength ● The polarization ● The incidence angle
Surface scattering
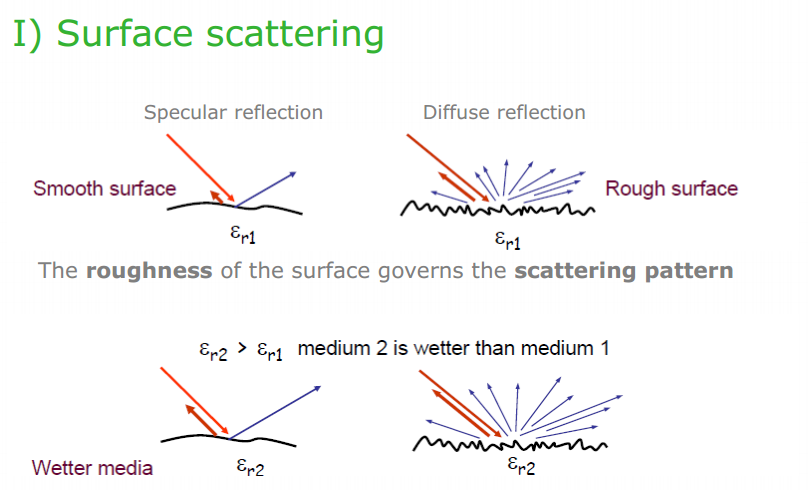 The moisture content (dielectric constant) of the medium governs the strength of the backscatter
The moisture content (dielectric constant) of the medium governs the strength of the backscatterSurface roughness
Shell’s law 相对粗糙度: ==same surface: rougher in short wavelength, smoother in long wavelength==
Dielectric Constant介电常数
Complex dielectric Constant (ε)
- ratio of the permittivity(介电常数) of a material to the permittivity of free space 自由空间的介电常数和材料的介电常数相比
- In other words: indicator of the ==reflectivity of a material==
- ==increasing ε leads to increasing backscatter==
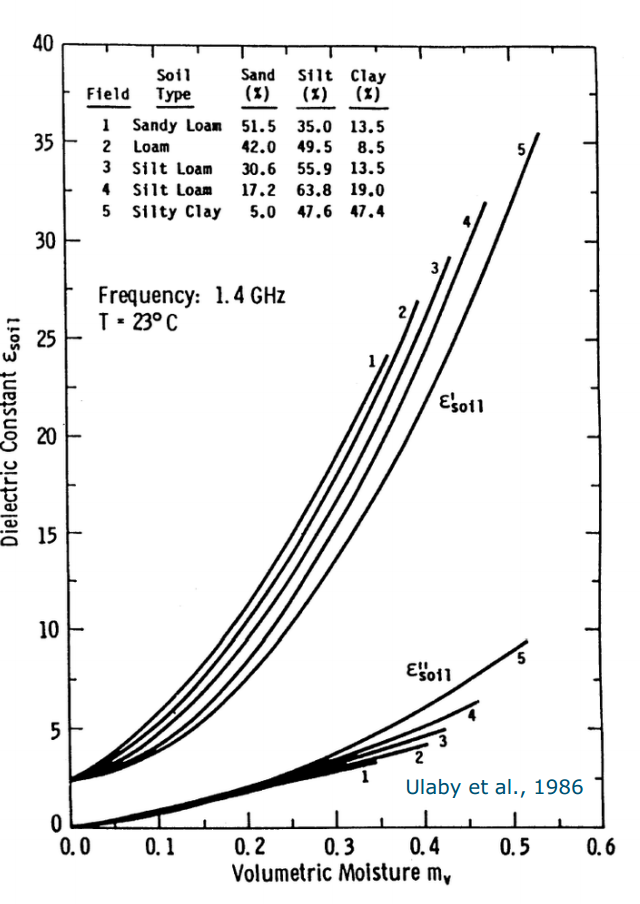
例子
- 介电常数的波动(fluctuation) Water is purple, because the wave of the water » wind Soil: large ε fluctuations (rain, dry) Forest: stable ε (saturated forest canopy)
- Ancient river network» dry sand/dry snow»Complex dielectric Constant (ε)=2-3» high permittivity
- Strong drop under freezing conditions» from water(80) to ice(3-4)
Volume scattering
- Concept: Inhomogeneous medium (canopy): Each inhomogeneity (leaves, branches) scatters incident wave in different directions
- Multiple scattering leads to depolarisation去极化 and attenuation 衰退of the signal
- ==Main source of VH and HV scattering==
- Increasing backscatter with increasing dielectric constant
Depolarization
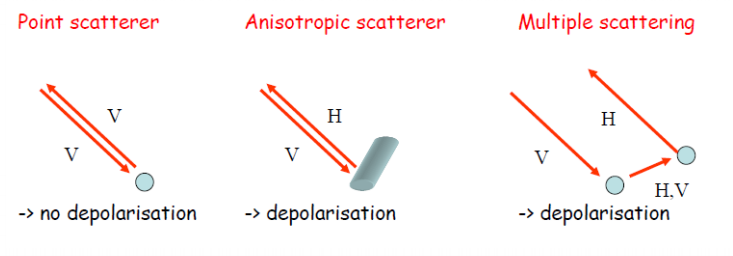
- Change in the orientation of the electric field during a reflection with curved scatters’ such as disc or cylinders 圆柱体 弯曲散射体(如圆盘或圆柱体)反射时电场方向的变化。
- Mainly occurs due to multiple scattering
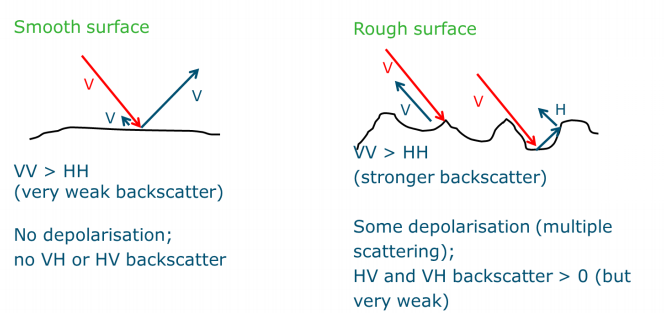
Single-bounce scattering
- Direct scattering from tree elements
- ==VV > HH==
- Some depolarisation, but very small (VH, HV)
Double-bounce scattering
- Concept: Two smooth surfaces form a right angle facing the radar beam
- ==HH > VV==
- Some depolarisation; HV and VH backscatter > 0 (but very weak)
Forest structure
Penetration depth and key forest scatterers Understory » Volume Mangroves HH double bounce»Brightening of the forest during inundation
Signal recovery ,not forest recovery VV/ VH Height is diffcult to recover
We cannot detect the man made or natural
HH : double-bounce VV : Single-bounce HV and VH: Volume Surface : dielectric constant
文档信息
- 本文作者:Xinyi He
- 本文链接:https://buliangzhang24.github.io/2024/01/22/Advanced-Earth-Observation-7.Radar-remote-sensing-for-forest-monitoring/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)
