used for classification
Motivation
- linear regression
- quantitative vs. qualitative(categorical) data quantitative data > regression quantitative Y qualitative data> classification qualitative Y class and regression can be used together
Why not linear regression
- in case of variable Y with >2 categories: Coding categories as numbers (ordering and distance between categories) is arbitrary
- In case of variable Y with 2 categories: Coding with 0/1 would work
- Even with 2 categories there is an issue: Example: credit card default / not default 但是还是不好predict probability
The Logistic Model
main idea: predict probability P(Y=1| X=..)
Logistic function
- S-shaped curve between 0 and 1:
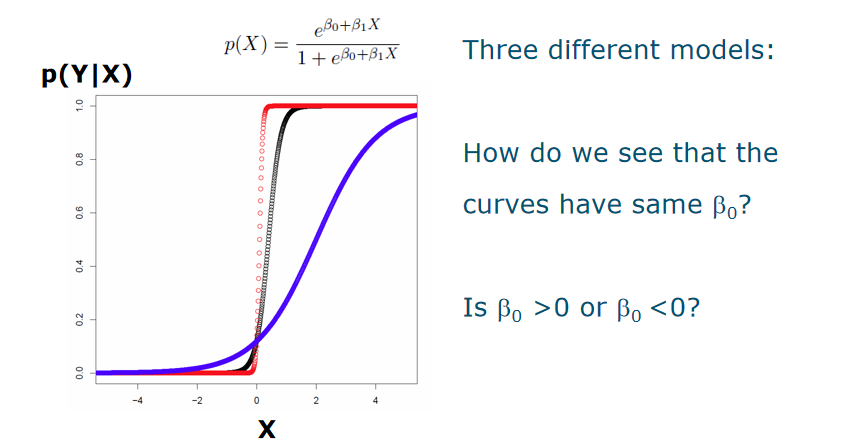
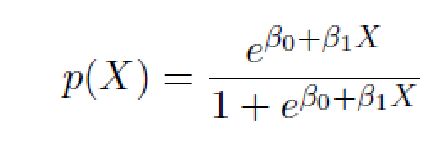 这里Linear regression 范围会小于0,但是它的意义是概率
这里Linear regression 范围会小于0,但是它的意义是概率 - How do we see that the curves have same B0? They cross the x= 0 at same point
- Is B0 >0 or B0 <0? if at the mentioned point the Y value is smaller than 0.5 , the B0<0
 temperature of meidian low and high
temperature of meidian low and highOdds
The ratio of the probability of one event to that of an alternative event
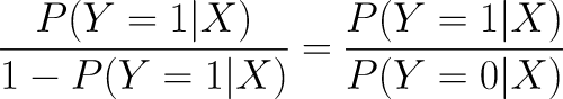
Logistic function leads to logit that is linear in X
Logit = log(Odds)
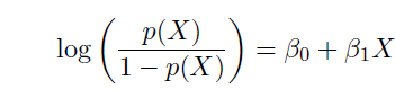 B1 in linear regression: gives average change of Y associated with one-unit increase in X B1 in logistic regression: gives average change of log odds (logit) with one-unit increase in X
B1 in linear regression: gives average change of Y associated with one-unit increase in X B1 in logistic regression: gives average change of log odds (logit) with one-unit increase in X
Exercise 9 (a)on average, what fraction of people with an odds of 0.37 of defaulting on their credit card payment will in fact default? (b)suppose that an individual has a 16% chance of defaulting on her credit card payment.What are the odds that she will default? 1 is default,越小越不default 0.37= x/1-x x= 0.16/1-0.16
Multiple Logistic Regression
how can we set decision boundary?this line will be 0.5?
Qualitative predictors
- 用dummies Number of dummy variables one lower than number of levels the variable has??????
Parameter Estimation
Maximum likelihood:
定义:
- maximum likelihood: general approach to estimate model parameters用于估计参数的值,使得给定参数下数据观测到的概率(即似然函数)最大化
- Basic idea: the experimental observations are those that are likely to be observed
- Hence: find values for parameters such that the ==probability of the observed data is as large as possible==
- Likelihood: probability of the data given the parameters
- Define Likelihood L (for N datapoints) L=![[Pasted image 20240214112727.png]] The assumption of L : independent Optimal parameters given data: those that maximize L BUT,Instead of maximizing L, maximize log(L)
推导:

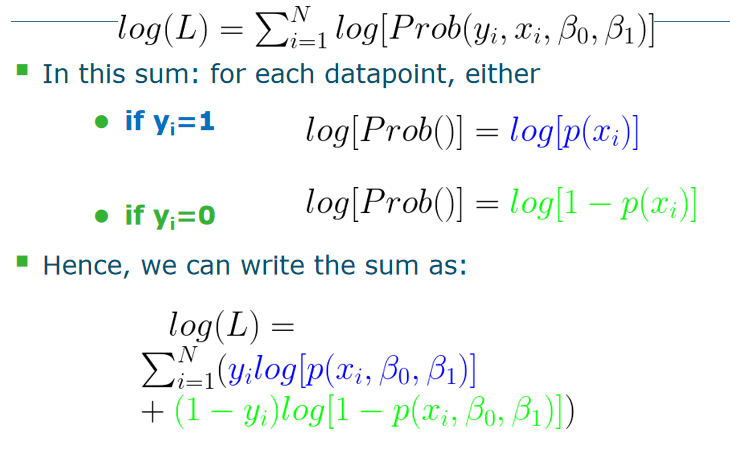
最后:
当log(L)的负值最小(NLL negativate log-likelihood)的时候,或者Log-likelihood 的值最大的时候(就是越大越好,但是值是负的),逻辑函数通过优化算法(literative algorithm)之后,找到最好的b1,b2这些参数。
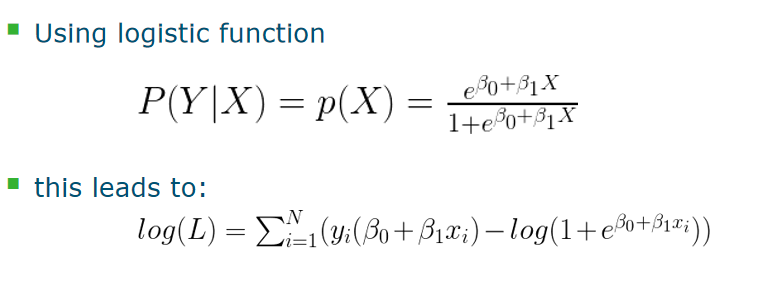 这个式子的变形是:log (p /1−p) = β0 + β1X1 + β2X2 这里面的p的含义是
这个式子的变形是:log (p /1−p) = β0 + β1X1 + β2X2 这里面的p的含义是  这个才我们要maximize的
这个才我们要maximize的Some Consideration
Interpretation of coefficient
跟Linear regression 差不多,instead of t-statistic, we use Z-statistic
Stability of parameter estimates
problem:
当模型参数的值发生变化时,模型的预测结果也会发生变化。如果模型参数的变化很大,那么模型的预测结果也可能会变得不稳定,即使输入数据没有变化。这种情况下,模型的参数估计是不稳定的。
solution:
regularization 通过在模型的损失函数中添加一个正则化项(regularization term),来限制模型参数的大小。这样可以降低模型参数的变化幅度,提高模型的稳定性。常用的正则化方法包括L1正则化(Lasso)和L2正则化(Ridge)等。
Multiple predictors
confounding
- confounding: a third variable (not the independent or dependent variable of interest) distorts the observed relationship between the variables of interest
- 为什么在引入income 变量之前student 的coefficient是正的,但是没引入这个变量之前student的coefficient是负的? 因为:confounding
Multinomial logistic regression
![[Pasted image 20240214222136.png]]
Softmax regression
Exercise ![[Pasted image 20240214222524.png]] (b)log (p /1−p) = β0 + β1X1 + β2X2
Recap:
Prediction of categorical Y given its features X is called…..classification Logistic regression: assume linear function for ……odds Parameter estimation: maximum likehood
文档信息
- 本文作者:Xinyi He
- 本文链接:https://buliangzhang24.github.io/2024/02/05/MachineLearning-3.Logistic-Regression/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)
