Clustering methods–Hierarchical
- dissimilarity matrix(cluster)dengrogram(cut)clustering
- bottom-up or agglomerative(as opposed to top-down or divisive)
- Disadavantages: once clustered, objects stay clustered, hard clustering: objects are assigned to a single cluster
Clustering methods–K-means
Data, Criterion, Clusters K(cluster)Clustering For every selected number of clusters K, choose optimal clustering What is optimal?
K-means definitions
- 都是并集,clusters do not overlap
- Optimal clustering:squared distances between all pairs in each cluster or, equivalently, squared distances to cluster means, are minimal
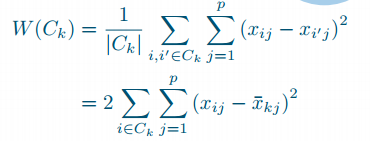
- problem: need known W(C_k), but there are possibilities (!)
- iterative optimization
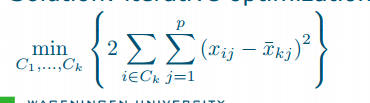
K-means algorithm
就是k means是表示xi只属于一个簇,所以我定下有k个簇,我随机把数据点放到这些簇里,然后求每个簇的平均值(和方差),找离这个簇最近的点,迭代一遍所有点,让分类的结果最后不变
- Choose number of clusters K and randomly assign each sample to a cluster
- Iterate until nothing changes: (a) for each cluster, calculate the centroid (mean) (b) re-assign each sample to the cluster whose mean is closest (in the Euclidean sense)
- Guaranteed to only decrease the criterion (why?):这个过程可以保证每次迭代都至少不会增加目标函数的值。 exercise 3

Choice of K
Rule of thumb: look for “drop” in criterion
K-means problems
Clusters can lose all samples
Why
- 初始质心选择不当:如果初始质心选取不当,有些质心可能会被分配到一个不包含任何样本的区域。这会导致该簇失去所有的样本。
- 非凸形状的簇:如果数据集包含非凸形状的簇,例如环状或月牙形状的簇,K-means 算法可能会将其分割成多个较小的簇,导致某个簇失去所有的样本。
- 数据量不均衡:如果某个簇中的样本数量太少,而其他簇中的样本数量较多,则某个簇可能会失去所有的样本,因为K-means 算法的更新过程是基于样本的平均值。
Solutions
- remove cluster and continue with K – 1 means
- alternatively, split largest cluster into two or add a random mean to continue with K means
Clustering result depends on initialization –Algorithm can get stuck in local minima
Solution:
- start from (many) different random initialisations
- keep the best clustering(lowest sumW(C_k))
Limitations
K-means model not necessarily optimal Equal cluster models not necessarily optimal Hard clustering not necessarily optimal exercise
The K-means model
What cluster model actually underlies K-means? ● spherical, uniform ● implicit in criterion Choosing an explicit model can help to: ● understand the result ● quantify the model fit ● try alternative models ● make assumptions explicit
Mixture Models
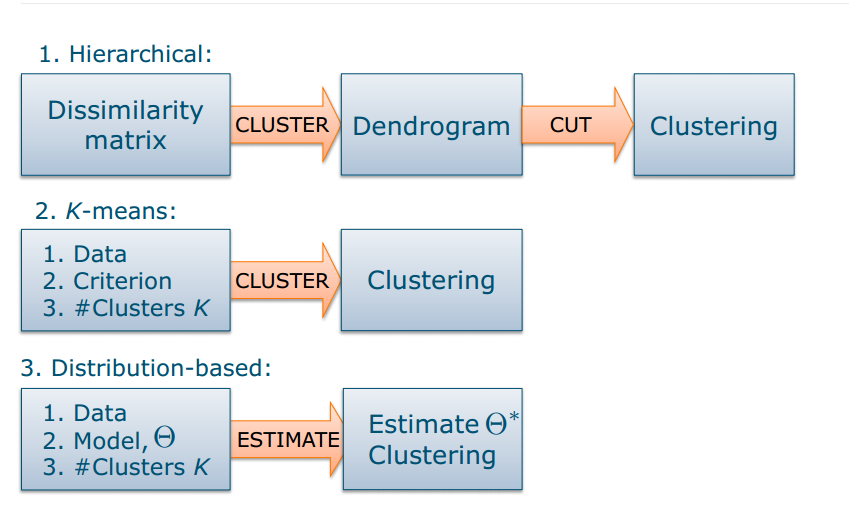
Model the probability distribution of the data
- gives model for overall data distribution
- "soft" clustering: captures uncertainty in assignments
- parameters can be found using maximum likelihood
Distribution-based clustering
- Each cluster is described by a probability density function
- Total dataset described by a mixture of density functions
- Clustering means maximizing the mixture fit,
- cluster assignment is based on posterior probabilities 就是我要知道x这个点属于每个簇的概率,把x分配给概率最高的簇,但是给定k簇的情况下求x(就是已经知道一个点属于k,求这个点是x点的概率)更好求(高斯的分布的密度函数求,就是用平均值和平方和求),所以先求这个。

Fitting mixture models
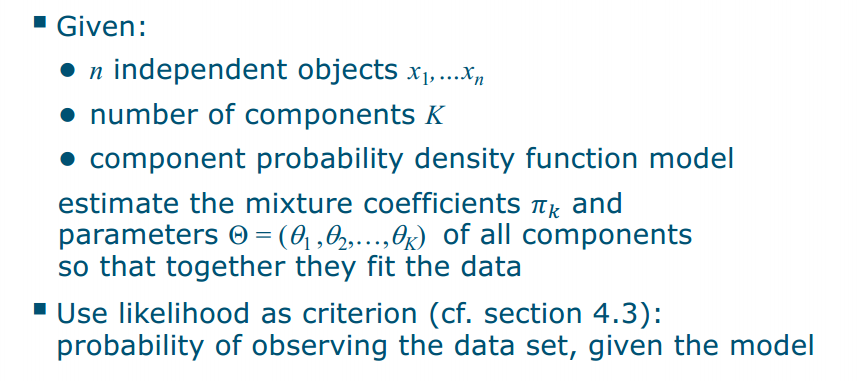 对于混合高斯模型,我们有以下步骤:
对于混合高斯模型,我们有以下步骤:- 初始化参数:我们首先随机初始化每个高斯分布的均值、方差和权重。
- 计算每个样本属于每个高斯分布的概率:对于每个样本xi,我们计算它属于每个高斯分布 k 的概率 P(xi∣k)。(Note that mixture models also work for other component densities!)
- 更新参数:对于每个高斯分布 k,我们根据每个样本属于该分布的概率来更新均值、方差和权重。这个更新过程使用最大似然估计的方法。(说白了就是选最大的概率)
- 重复步骤2和3:我们重复步骤2和3,直到参数不再改变或达到最大迭代次数。
- 输出参数:最终,我们输出参数的估计值,这些参数可以用来描述数据的分布情况。
Mixture of Gaussians
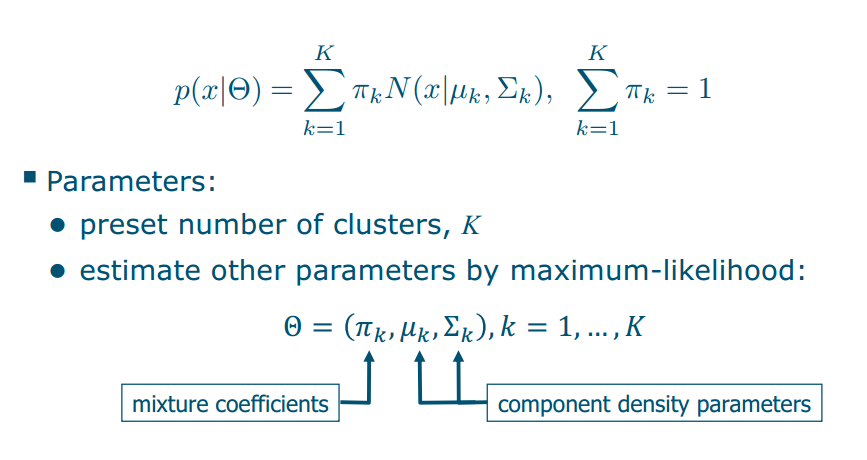
Latent variable
Problem:
need to simultaneously estimate two interdependent things… no closed form solution! cluster membership of each object
solutions

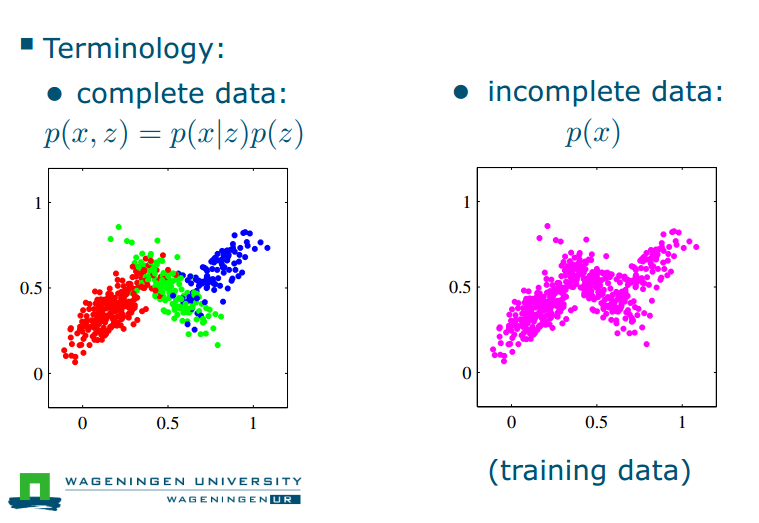
The EM algorithm
Expectation-Maximization algorithm:
- general class of algorithms for this type of problem
- repeatedly: recalculate cluster membership of each sample (E) recalculate density parameters of each cluster (M) EM算法是一种求解含有隐变量的概率模型的参数估计方法。它的基本思想是:假设观测数据的生成过程包含两个步骤,即隐变量的生成和观测数据的生成。在E步,算法利用当前参数估计隐变量的后验概率,即估计隐变量的分布;在M步,算法利用E步的结果估计模型参数。通过反复迭代E步和M步,最终达到收敛。EM算法的目标是最大化似然函数,使得观测数据的生成概率最大,从而得到最优的参数估计。
The EM algorithm for MoGs
EM 就是隐变量的概率我知道(但是会随着高斯分布的均值和协方差变化而变化),求浅变量的概率就是求responsibility,(把这个代入这个高斯求浅变量的式子里面就是Estep),用最大似然法找到最大的(把式子求导找极值)就是Mstep
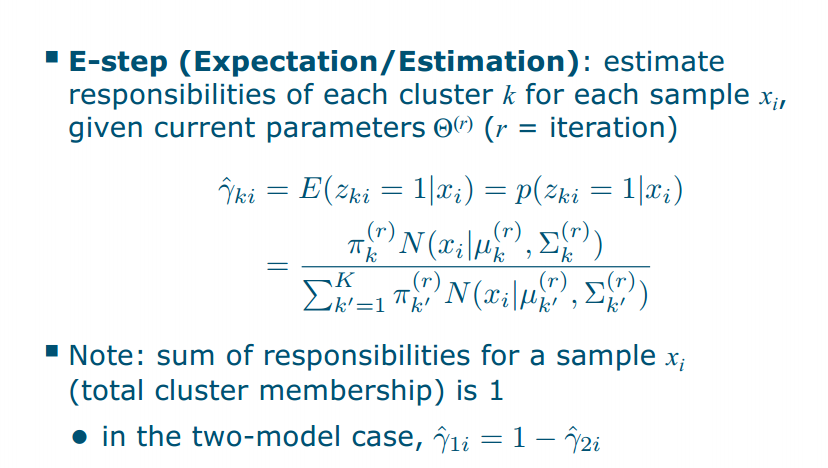
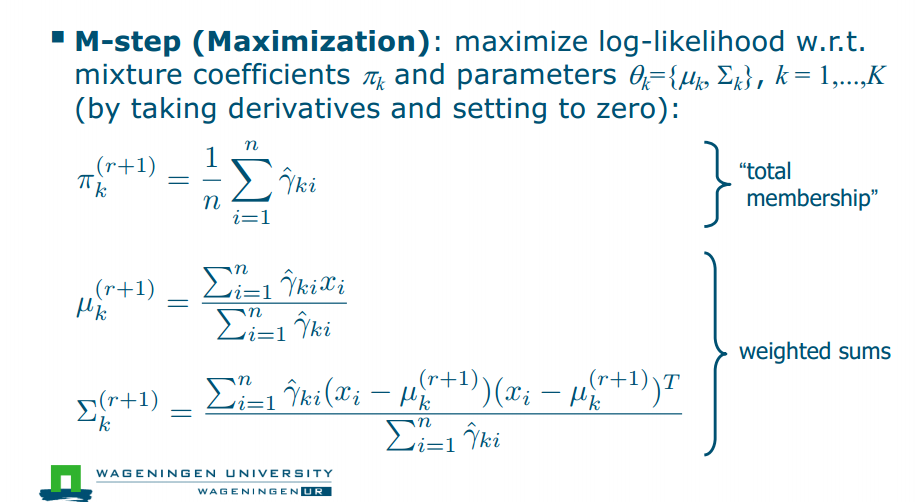 EM 就是隐变量的概率我知道(但是会随着高斯分布的均值和协方差变化而变化),求浅变量的概率就是求responsibility,用最大似然法找到最大的(在M步中,我们通过最大化似然函数来更新模型参数估计,例如我们可以通过对似然函数求导,令导数为0,找到似然函数的最大值点,这个过程通常称为最大似然估计(MLE))
EM 就是隐变量的概率我知道(但是会随着高斯分布的均值和协方差变化而变化),求浅变量的概率就是求responsibility,用最大似然法找到最大的(在M步中,我们通过最大化似然函数来更新模型参数估计,例如我们可以通过对似然函数求导,令导数为0,找到似然函数的最大值点,这个过程通常称为最大似然估计(MLE))
K-means is a special case of a mixture-of-Gaussians 如果每一个点,到每一个簇的概率都是相等的,就是Kmeans,但是如果不是相等的,就是mog。 在K-means算法中,每个簇的协方差矩阵是对角矩阵,并且每个元素相等。
Limitations
- Disadvantages (similar to K-means): ● depends on initial conditions, can get stuck in local minima: same solution局部最优 ● convergence can be slow收敛很慢 ● problems with covariance estimates: if too few samples are members of a cluster, there will not be enough data to base estimate on 样本太少
- Advantages: ● simple to implement简单 ● can use prior knowledge of cluster distribution可以用先验概率
