The Managerial Perspective
1 components of organizational memory and then discussing some of its common problems. 2 the relationship between information and organizational goals
Newell-Simon Model the augmented human information processing model becomes a pattern for an organizational information precessing system 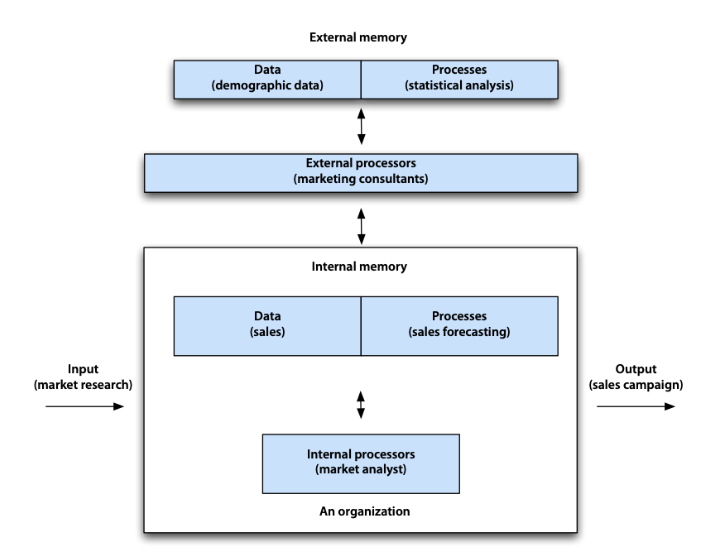
Chapter 1 Managing Data
Memory system
Individual data management
interval memories exterval memories: to do list : the some features commom to all data management systems: storage medium, structure for storing data, interface for rapid data entry and retrieval
Organizational data management
Types of information systems
The information systems cycle
Desirable attributes of data
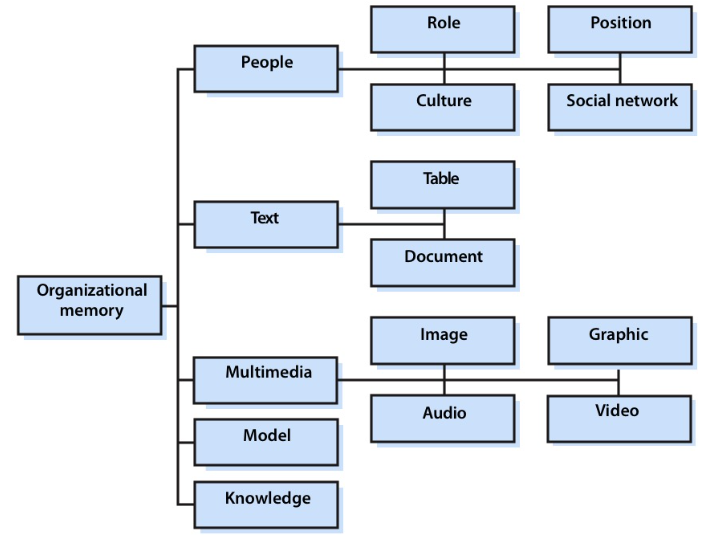
Components of organizational memory
Problems with data management systems
redundancy, lack of data control, poor interface, delays, lack of reality, lack of data integration
Chapter 2 Information
This chapter has some good parts and some arguable ones. It presents a very partial view of information. For instance, information is also a commodity of power, as you will probably have experienced. Also, there is more to decision making than information. There are many viewpoints in this chapter that could be questioned. Furthermore, the focus is very much on business information. Research institutes function in a somewhat different way. Still, if you change “manager” into “research client” much remains valid
A historical perspective
A brief history of information systems
Information Characteristics
hardness, richness, class(content, form, behavior, and action)
Information and organizational change
goal-setting information, planning, benchmarking,gap information, problem identification,scorekeeping,change information, problem solution, information as a means of change, marketing,customer service, empowerment,
Information delivery systems
Information intergration
Knowledge
Section2 Data Modeling and SQL
Chapter 3: The Single Entity
Note: Entity-Relationship diagramming key skills : data modeling and query formation Data definition language(DDL) Data manipulation language(DML) Structured Query Language (SQL)
Creating a single-table database
entity一个表是entity entity name becomes the table name identifier becomes the primary key attributes就是一个column instance 这个表里面的一行就是freedonia copper是一个instance
Defining a table
| VARCHAR(n) | A variable-length string of up to n characters | | ———- | ———————————————- | open diamond indicate the column can be null closed diamond indicate the column must have a value
Inserting rows into a table
Querying a single-table database
<>不等于 和a BETWEEN x AND y等于 a >= x AND a <= y
IN 和or相等
SELECT * FROM share WHERE shrcode IN ('FC','AR','SLG');
SELECT * FROM share
WHERE shrcode = 'FC' or shrcode = 'AR' or shrcode = 'SLG';
NOT IN 和<>相等
SELECT * FROM share WHERE shrcode NOT IN ('CS','PT');
SELECT * FROM share WHERE shrcode <> 'CS' AND shrcode <> 'PT';
Ordering columns
Ordering rows
SELECT * FROM share WHERE shrpe >= 10
ORDER BY shrpe DESC, shrfirm;
按照shrpe的大小来降序排列 数据的类型,根据numeric 来排列和根据characher来排列是不同的
Derived data
SELECT shrfirm, shrprice, shrqty, shrdiv/shrprice*100 AS yield FROM share;
因为yield可以根据前面的这几个计算,所以只需要在view的时候算给他就行了,不需要给它作为一个列
Aggregate functions
COUNT
SELECT COUNT(shrfirm) AS bigholdings FROM share WHERE shrqty > 50000;
AVG-averaging SUM MIN MAX
Subqueries
SELECT shrfirm, shrpe FROM share
WHERE shrpe > (SELECT AVG(shrpe) FROM share);
经典错误 SELECT shrfirm, shrpe from share WHERE shrpe > avg(shrpe); ==你不能在WHERE子句中直接引用聚合函数结果作为过滤条件==
Regular Expression
search for a string List all firms containing ‘Ruby’ in their name
SELECT shrfirm FROM share WHERE shrfirm REGEXP 'Ruby';
search for alternative strings
SELECT shrfirm FROM share WHERE LOWER(shrfirm) REGEXP 'gold|zinc';
search for beginning string/ending string ‘^Sri’/ ‘geese$’
DISTINCT
eliminating duplicate rows
SELECT DISTINCT shrpe FROM share;
unique
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT shrpe) as 'Different PEs' FROM share;
DELETE
DELETE FROM share WHERE shrfirm = 'Burmese Elephant';
UPDATE
UPDATE share SET shrprice = 31.50 WHERE shrcode = 'FC';
2a SELECT name, code FROM share 2d. SELECT * FROM share WHERE price < 1 2c. SELECT name, price FROM share WHERE price >=10 2d. SELECT firm name, price, holding, firm name * price * holding AS total FROM share
2e. SELECT name, price/ holding* 100 AS yield FROM share WHERE yield >5 2f. SELECT dividend * quantity AS totaldiv FROM share WHERE code = ‘PT’
2g. SELECT * FROM share WHERE price < dividend * 20 2h.==subqueries== SELECT price/ holding* 100 AS yield FROM share WHERE yield >(SELECT MIN(yield) FROM share)
2i, SELECT SUM(price) FROM share WHERE PEratio >10 2j.
Chapter 4 The One-to-Many Relationship
natcode是stock的外键,因为它是nation的主键,natcode是斜体,红色菱形(外键) every foreign key must have a matching primary key primary key is non-null but foreign key can null
PRIMARY KEY(stkcode),
CONSTRAINT fk_has_nation FOREIGN KEY(natcode)
REFERENCES nation(natcode) ON DELETE RESTRICT);
限制两个表里的同一列的值相同,就是natcode是它的外键而不允许删除。
Querying a two-table database
Join
两个表里都各有一个部分我们想要,组成一个新表的时候 虽然这个列(一个表里的FK,另一个表里的PK),但是查询的时候要写table名。
SELECT natname, sum(stkprice*stkqty*exchrate) as stkvalue
FROM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode
GROUP BY natname;
GROUP BY - reporting be groups
List stocks by nation, and for each nation show the number of stocks for each PE ratio and the total value of those stock holdings in UK pounds. SELECT natname, stkpe, COUNT(), SUM(stkprice stkqty*exchrate) AS stkvalue FROM stock,nation GROUP BY natname, stkpe;
list stocks by nation (就是GROUP BY natname, stkpe, 换句话说,每个不同的 (natname, stkpe) 组合将被视为一个分组), and for each nation show the number of stocks for each PE ratio(SELECT natname, stkpe, COUNT(* ))这个COUNT计数的(natname, stkpe)组合的计数 and the total value of those stock holdings in UK pounds(SUM(stkprice * stkqty * exchrate) AS stkvalue)
HAVING
HAVING in GROUP BY 就像是WHERE in SELECT HAVING 前面始终是 GROUP BY,后面始终是函数(SUM、AVG、MAX、MIN 或 COUNT)
Regular expression- pattern matching
不含specified charachters的string :
SELECT natname FROM nation WHERE LOWER(natname) REGEXP '[^a-z]'
repeated pattern or repetition
SELECT stkfirm FROM stock WHERE stkfirm REGEXP '[e]{2}';
combining alternation and repetition multiple versions of a string
WHERE LOWER(stkfirm) REGEXP '[io]nia';
string in a particular position
WHERE LOWER(stkfirm) REGEXP '^(.){2}t';
string not containing any specified characters
WHERE LOWER(natname) REGEXP '^[^s]*$'
Subqueries
Outer query SELECT stkfirm FROM stock WHERE natcode IN Inner query (SELECT natcode FROM nation WHERE natname = ‘Australia’) 在inner query里面就不必implicity qualified as nation.natcode了 在outer query里面就默认是stock.natcode
correlated subquery
SELECT natname, stkfirm, stkqty FROM stock JOIN nation
ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode
WHERE stkqty >
(SELECT avg(stkqty) FROM stock
WHERE stock.natcode = nation.natcode);对每个国家算它这个国家的平均股票水平
Views- virtual tables
CREATE VIEW stkvalue
(nation, firm, price, qty, exchrate, value)
AS SELECT natname, stkfirm, stkprice, stkqty, exchrate,
stkprice*stkqty*exchrate
FROM stock JOIN nation
ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode;
A view can be used in a query
SELECT nation, firm, value FROM stkvalue WHERE value > 100000;
2a SELECT stkprice * stkqty * exchrate AS value FROM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode WHERE natname = ‘AUS’; 2b.Report the dividend payment of all stocks.???
SELECT stkcode, stkfirm, stkdivstkqtyexchrate FROM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode;
2c. SELECT natname, SUM(stkqty * stkprice) FROM stock, nation GROUP BY natcode;这里还是要用JOIN的
2d. CREATE VIEW value (nation, frim, stkprice, stkqty, exchrate, value, yield) AS SELECT natname, stkfirm, stkprice, stkqty, exchrate, FROM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode;
2e. SELECT natname,AVG(value.yield) FORM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode GROUP BY natcode; 2f. SELECT natname, MAX(value.yield), MIN(value.yield) FORM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode GROUP BY natcode;
==2g. ???==
SELECT natname, stkfirm, stkqty, stkpricestkqtyexchrate,stkdiv/stkprice100exchrate AS yield FROM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode WHERE yield > (SELECT avg(yield) FROM stock GROUP BY natname )
error Code: 1054. Unknown column ‘yield’ in ‘where clause’ 0.094 sec
SELECT natname, stkfirm, stkqty,stkpricestkqtyexchrate,stkdiv/stkprice100exchrate AS yield FROM stock JOIN nation ON stock.natcode = nation.natcode GROUP BY natname HAVING AVG(yield) > (SELECT AVG(yield) FROM stock);
Chapter 5 The Many-to-Many Relationship
The plus indicates that LINEITEM’s unique identifier is the concatenation of saleno and lineno When we have an m:m relationship, we create an associative entity to store data about the relationship. 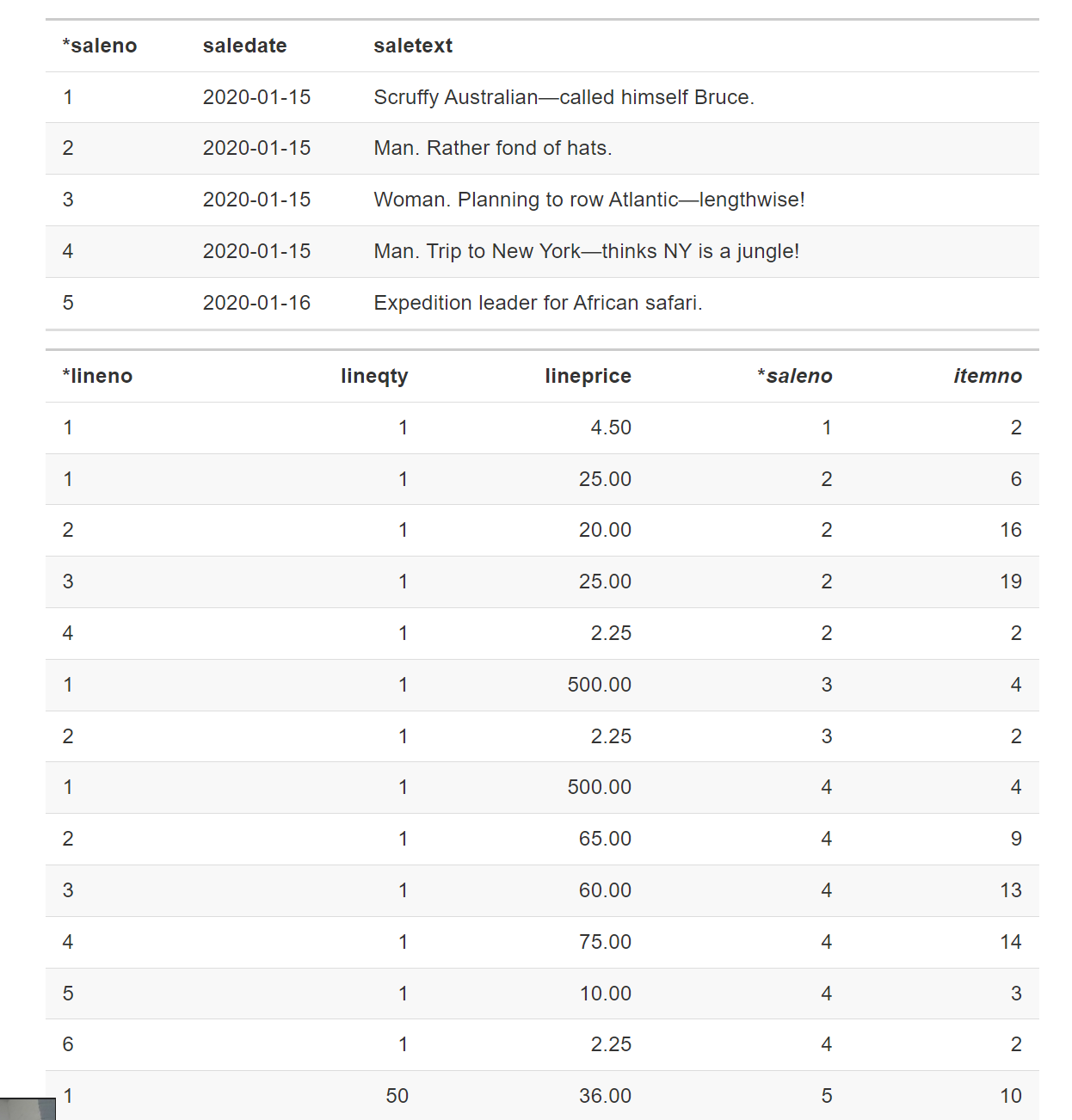
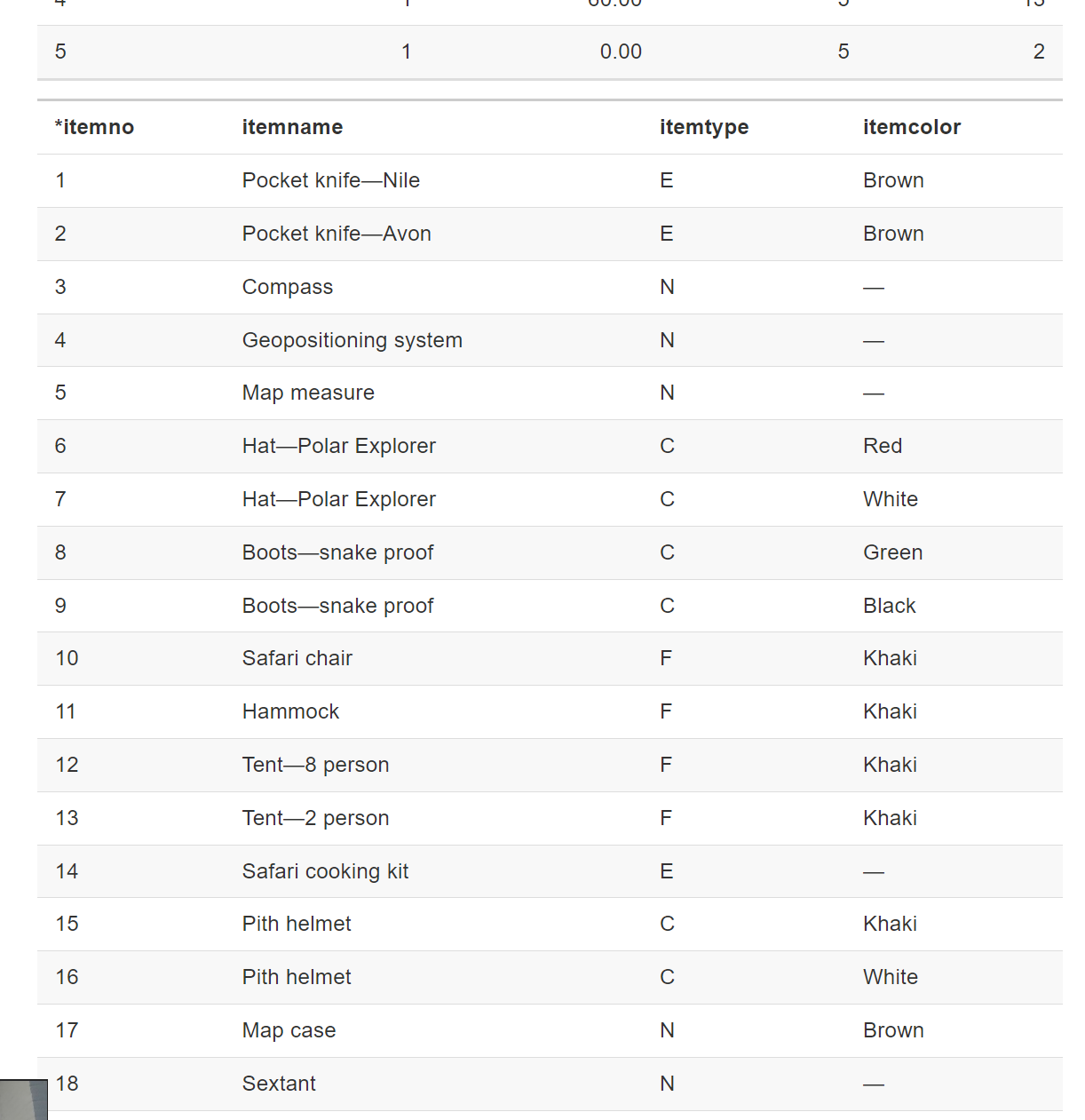
CREATE TABLE lineitem ( lineno INTEGER, lineqty INTEGER NOT NULL, lineprice DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL, saleno INTEGER, itemno INTEGER, PRIMARY KEY(lineno,saleno), CONSTRAINT fk_has_sale FOREIGN KEY(saleno) REFERENCES sale(saleno), CONSTRAINT fk_has_item FOREIGN KEY(itemno) REFERENCES item(itemno)); Lineno位于两个1 : m关系的many 端。
Querying an m : m relationship
A three-table join: 三表连接
EXISTS 是否存在
at least one line meets a specified condition
SELECT itemname, itemcolor FROM item
WHERE itemtype = 'C'
AND EXISTS (SELECT * FROM lineitem
WHERE lineitem.itemno = item.itemno);
NOT EXISTS子查询来检查这些商品是否在lineitem表中没有对应的条目。如果没有对应的条目,则这些商品符合查询的条件,将会被返回。 all rows do not satisfy a specified condition
SELECT itemname, itemcolor FROM item
WHERE itemtype = 'C'
AND NOT EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM lineitem
WHERE item.itemno = lineitem.itemno);
Divide除法/双重否定
Find the items that have appeared in all sales. forall
SELECT itemno, itemname FROM item
WHERE NOT EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM sale
WHERE NOT EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM lineitem
WHERE lineitem.itemno = item.itemno
AND lineitem.saleno = sale.saleno));
![[5292a4f30344f6a165751ec661d7cfd.png]]
Beyond the great divide
The query “Find the items that have appeared in all sales”
“Find the items for which the number of sales that include this item is equal to the total number of sales.” “Find items such that there does not exist a sale in which this item does not appear.”
如果某个 “saleno” 值在表 “sale” 中出现了多次,COUNT(DISTINCT saleno) 将会计算这个 “saleno” 值为一个唯一值,而不会重复计算。因此,结果会告诉您有多少个不同的 “saleno” 值在表 “sale” 中出现了。
SELECT item.itemno, item.itemname
FROM item JOIN lineitem
ON item.itemno = lineitem.itemno
GROUP BY item.itemno, item.itemname
HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT saleno)
= (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT saleno) FROM sale);
Set Operations
UNION or INTERSECT and
3
List the names of items for which the quantity sold is greater than one for any sale.
Compute the total value of sales for each item by date.
Report all items of type “F” that have been sold.
List all items of type “F” that have not been sold.
Compute the total value of each sale.
a SELECT itemno, itemname FROM item JOIN lineitem ON item.itemno = lineitem.itemno WHERE (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT itemno) FROM lineitem) >1 b. SELECT itemno, itemname FROM item JOIN lineitem ON item.itemno = lineitem.itemno lineitem JOIN sale ON lineitem.saleno = sale.saleno GROUP BY saledate HAVING (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT itemno) FROM lineitem) c. SELECT itemno, itemname FROM item WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sale WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM lineitem WHERE lineitem.itemno = item.itemno AND lineitem.saleno = sale.saleno AND itemtype = “F”)); d. SELECT itemno, itemname FROM item WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sale WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM lineitem WHERE lineitem.itemno = item.itemno AND lineitem.saleno = sale.saleno AND itemtype = “F”)); e. SELECT saleno, SUM(lineqty * lineprice)
FROM lineitem
GROUP BY saleno;
Chapter 6 One-to-One and Recursive Relationships
Modeling a one-to-one relationship
就是这个1:1是隐藏的,所以要把它标出来 大概就是一个boss可以用很多个employee 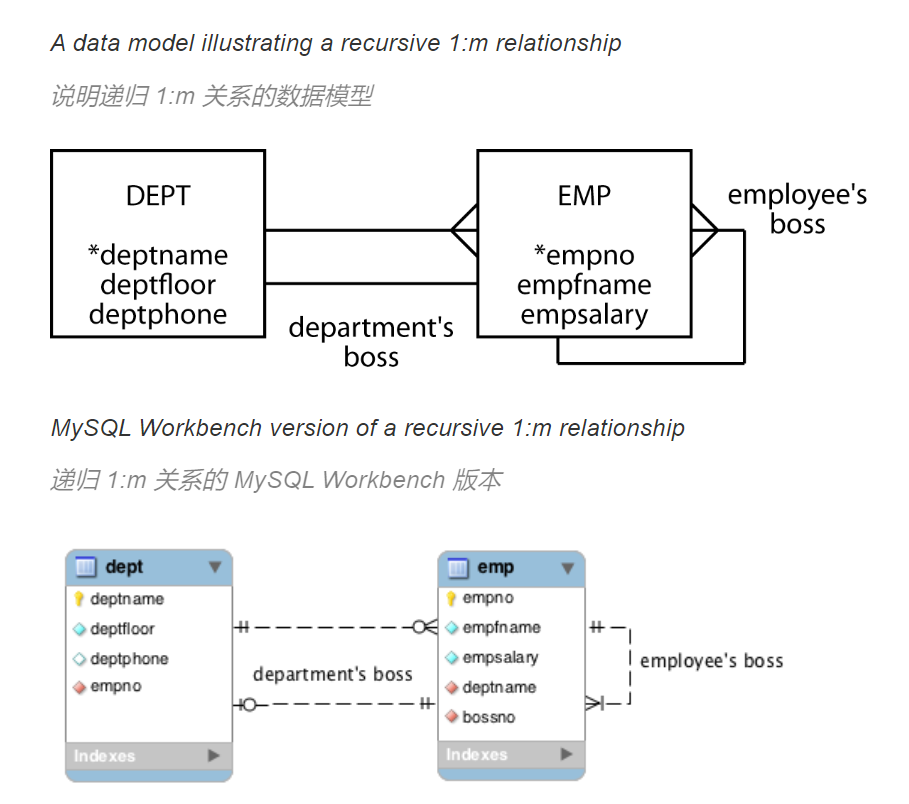
不同的表中进行的递归:Mapping a recursive one-to-many relationship
在many的那一端创建一个additional column as foreign key. In this case, empno is used, so we use bossno as the FK in empoly table 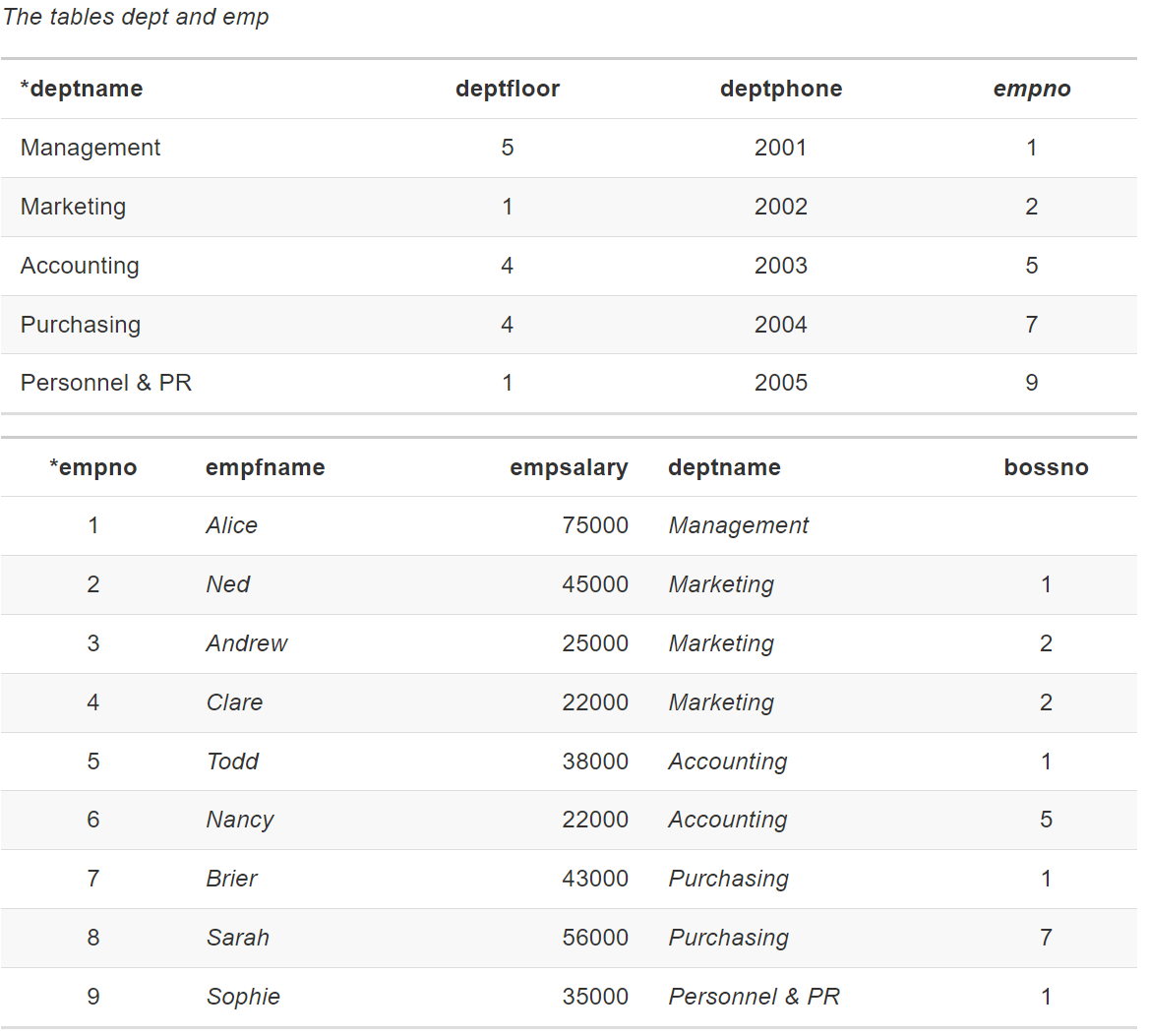 就是emp表里有deptname(另一个表的主键),能作为FK,还有一个附加列。 dep表里有empno(另一个表的主键)不能作为FK
就是emp表里有deptname(另一个表的主键),能作为FK,还有一个附加列。 dep表里有empno(另一个表的主键)不能作为FK
SQL
CREATE TABLE dept (
deptname VARCHAR(15),
deptfloor SMALLINT NOT NULL,
deptphone SMALLINT NOT NULL,
empno SMALLINT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(deptname));
CREATE TABLE emp (
empno SMALLINT,
empfname VARCHAR(10),
empsalary DECIMAL(7,0),
deptname VARCHAR(15),
bossno SMALLINT,
PRIMARY KEY(empno),
CONSTRAINT fk_belong_dept FOREIGN KEY(deptname)
REFERENCES dept(deptname),
CONSTRAINT fk_has_boss FOREIGN KEY(bossno)
REFERENCES emp(empno));
如果dep也定义deptname作为FK的话,那么就有两个约束就不对了,就是deadlock了
Self-Referential foreign key
note order
Query One-to-One Relationship
List the salary of each department’s boss
SELECT emfname, deptname, empsalary FROM emp WHERE empno IN (SELECT empno FROM dept);
(GROUP BY 用HAVING, SELECT 用WHERE, WHERE 用IN)
Querying a recursive 1 : m relationship
就是把两个表合到一起,就可以在同一行查询
Find the salary of Nancy’s boss.
WITH wrk AS (SELECT * FROM emp), boss AS( SELECT * FROM emp) SELECT wrk.empfname, wrk.empsalary , boss.empfname, boss.empsalary FROM wrk JOIN boss ON wrk.bossno = boss.empno WHERE wrk.empfname = ‘Nancy’;
Find the names of employees who earn more than their boss.
在同一个表里进行的递归Modeling a recursive one-to-one relationship
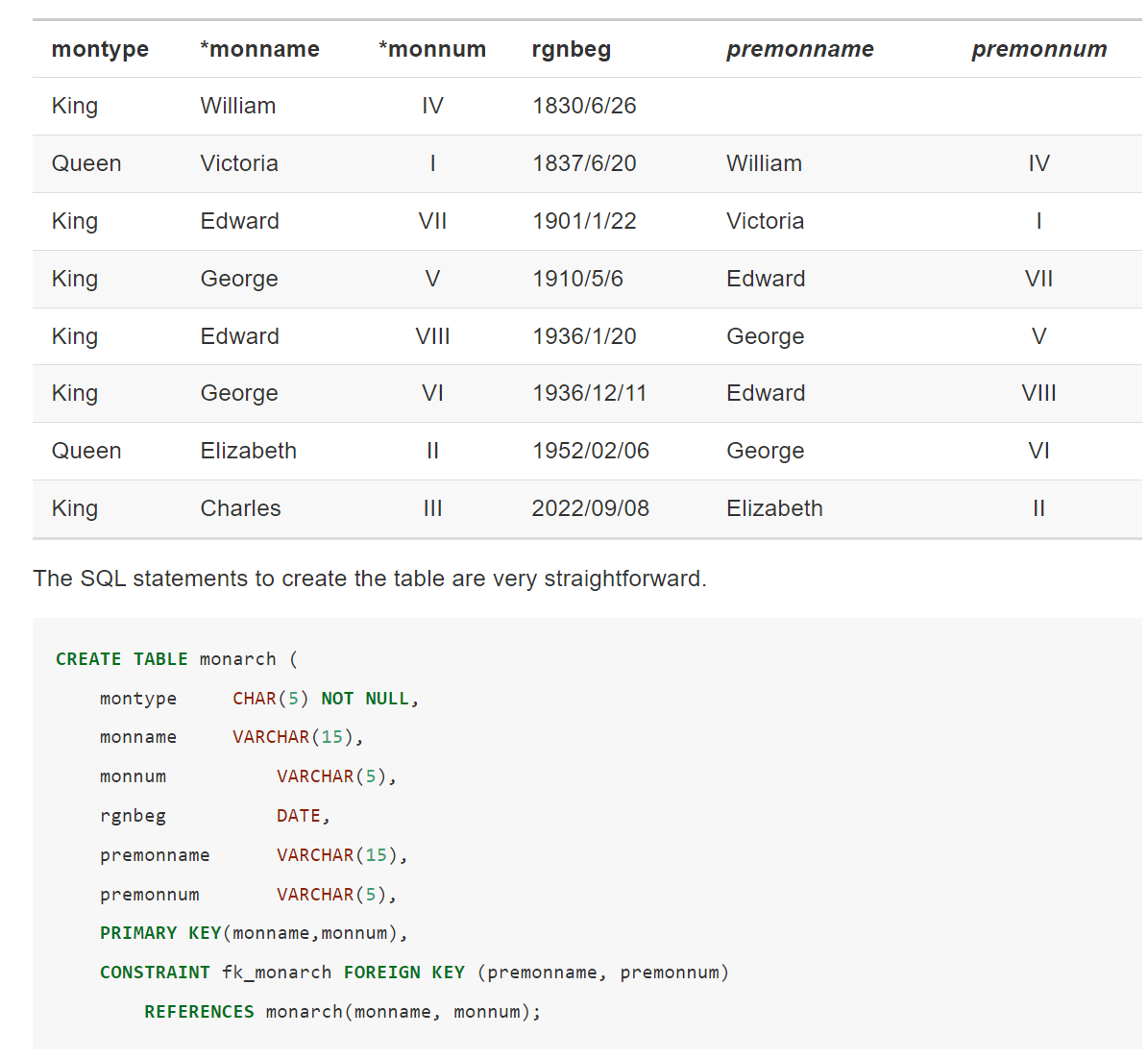 也可以用self referential
也可以用self referential
同一个表Querying a recursive one-to-one relationship
Was Elizabeth II’s predecessor a king or queen?
WITH
cur AS (SELECT * FROM monarch),
pre AS (SELECT * FROM monarch)
SELECT pre.montype FROM cur JOIN pre
ON cur.premonname = pre.monname AND cur.premonnum = pre.monnum
WHERE cur.monname = 'Elizabeth'
AND cur.monnum = 'II';
List the kings and queens of England in ascending chronological order.
SELECT montype, monname, monnum, rgnbeg FROM monarch ORDER BY rgnbeg(时间的那一列);
Modeling a recursive many-to-many relationship
两个表也可以表示m : m关系,因为就是商品,买家和销售列表是三个表,但是如果商品多一列附加列是买家的主键,就可以递归两个表表示m:m 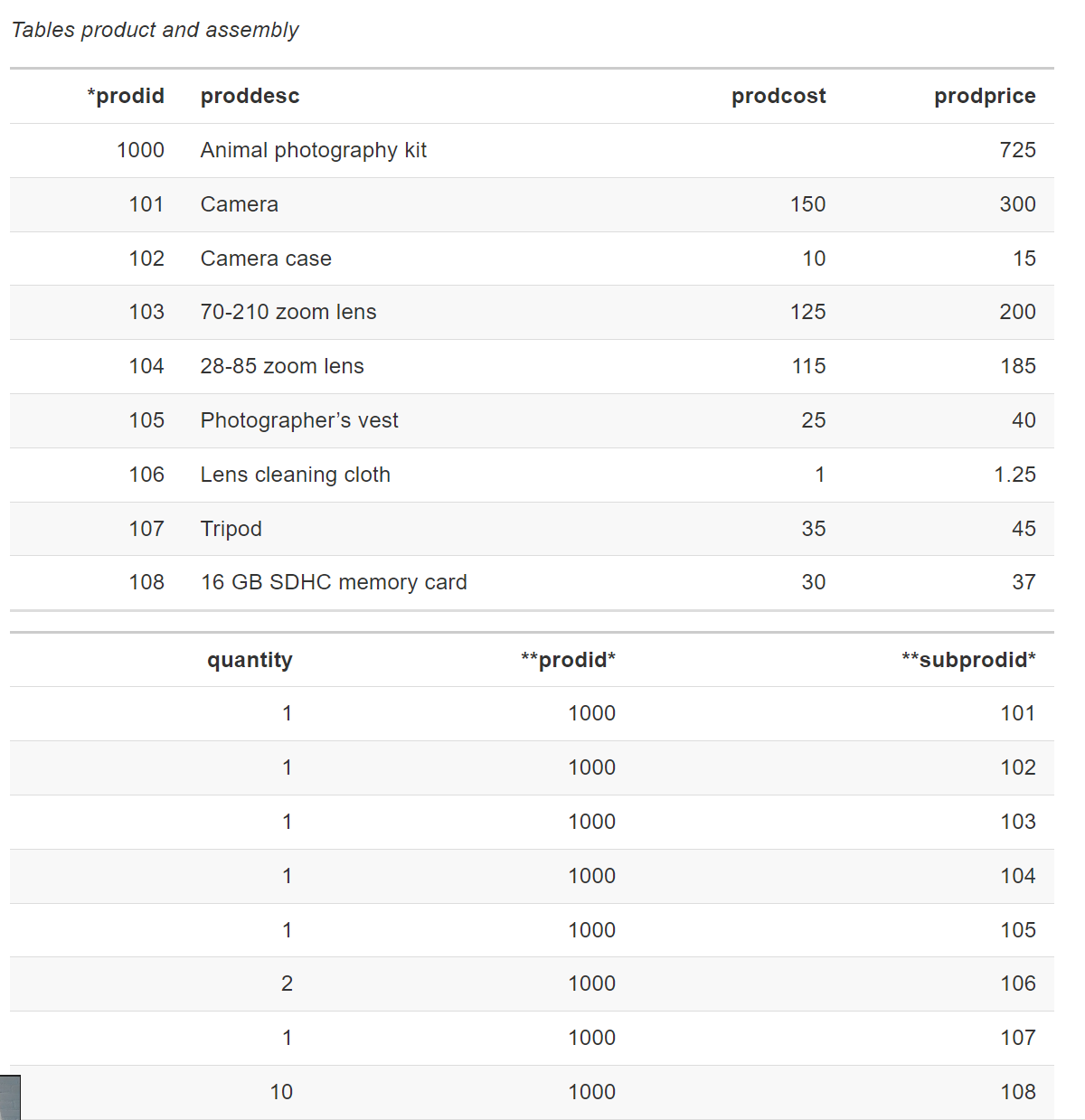
Mapping a recursive many-to-many relationship
CREATE TABLE product (
prodid INTEGER,
proddesc VARCHAR(30),
prodcost DECIMAL(9,2),
prodprice DECIMAL(9,2),
PRIMARY KEY(prodid));
CREATE TABLE assembly (
quantity INTEGER NOT NULL,
prodid INTEGER,
subprodid INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY(prodid, subprodid),
CONSTRAINT fk_assembly_product FOREIGN KEY(prodid)
REFERENCES product(prodid),
CONSTRAINT fk_assembly_subproduct FOREIGN KEY(subprodid)
REFERENCES product(prodid));
Querying a recursibe many-to-many relationship
List the product description and cost of each component of the animal photography kit.
可以用上面一样的方法
WITH
a AS (SELECT * FROM product),
b AS (SELECT * FROM product)
SELECT b.proddesc, b.prodcost FROM a JOIN assembly
ON a.prodid = assembly.prodid
JOIN b
ON assembly.subprodid = b.prodid
WHERE a.proddesc = 'Animal photography kit';
也可以用内部查询加外部查询
SELECT proddesc, prodcost FROM product
WHERE prodid IN
(SELECT subprodid FROM product JOIN assembly
ON product.prodid = assembly.prodid
WHERE proddesc = 'Animal photography kit');
Write SQL to answer the following queries using the DEPT and EMP tables described in this chapter: 使用本章中描述的 DEPT 和 EMP 表编写 SQL 来回答以下查询:
Find the departments where all the employees earn less than their boss. 找到所有员工收入都低于老板的部门。 WITH wrk AS (SELECT * FROM emp), boss AS (SELECT * FROM emp) SELECT wrk.deptname FROM dept JOIN wrk ON wrk.bossno = dept.empno JOIN boss ON boss. bossno = dept.empno WHERE wrk.empsalary < boss.empsalary;
Find the names of employees who are in the same department as their boss (as an employee). 查找与其老板(作为员工)在同一部门的员工姓名。
List the departments having an average salary greater than $25,000. 列出平均工资超过 25,000 美元的部门。
List the departments where the average salary of the employees, excluding the boss, is greater than $25,000. 列出员工平均工资(不包括老板)超过 25,000 美元的部门。
List the names and manager of the employees of the Marketing department who have a salary greater than $25,000. 列出营销部门年薪超过 25,000 美元的员工姓名和经理。
List the names of the employees who earn more than any employee in the Marketing department. 列出收入高于营销部门任何员工的员工姓名。
Chapter 7 Data Modeling
the scope of its business models technology» trigger data models are converted into relational database
Data Modeling
Building blocks
entity attribute relationship 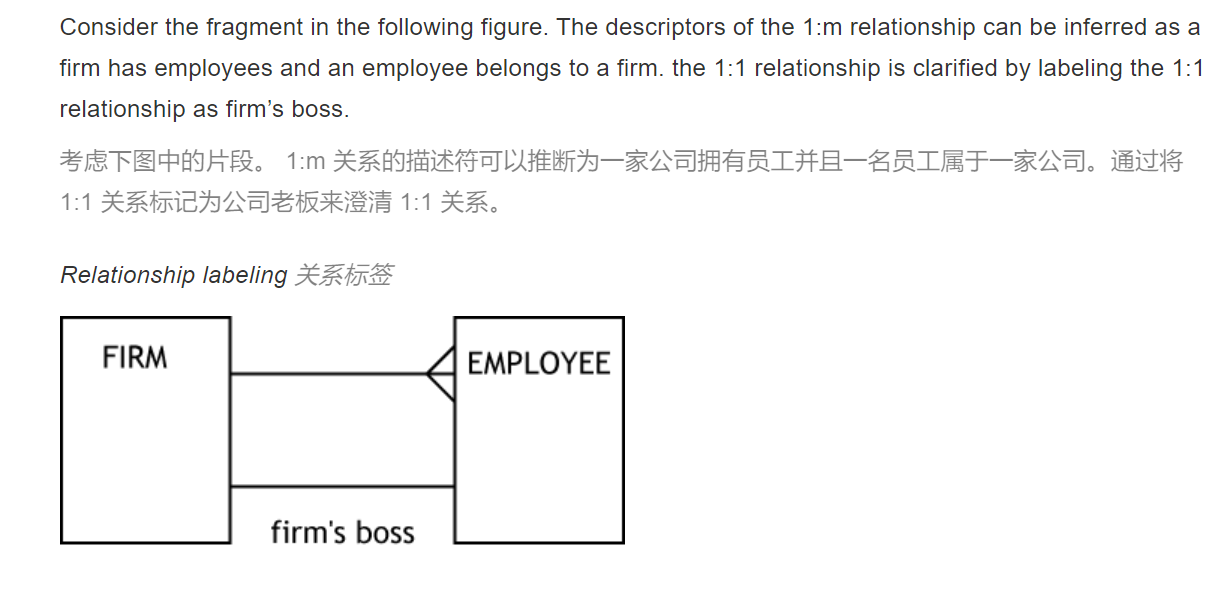 identifier
identifier 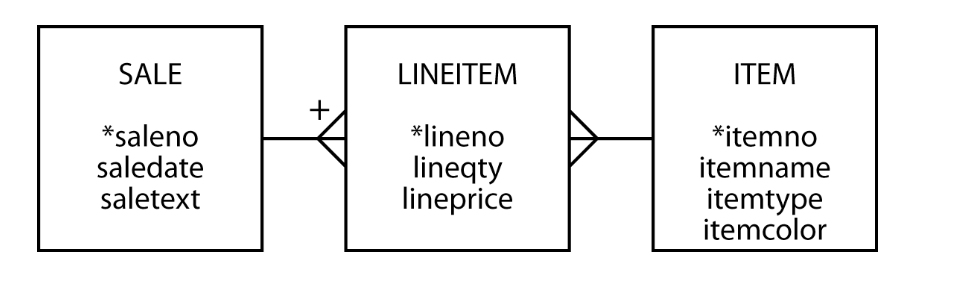 就是如果这个多端有一个加号的话,代表Lineno不能单独定义这个entity,需要saleno和lineno一起来定义这个entity
就是如果这个多端有一个加号的话,代表Lineno不能单独定义这个entity,需要saleno和lineno一起来定义这个entity
Data model quality
nation-stock a lesson in pure geography family matter book a history lesson aircraft leasing 就是generalize lease
Cardinality
![[8201500abdb57c50b9d5cfec6b5fb25.png]] 就是○是表示可选 横杆 | 是表示必须存在 ○靠近的一端是被可选的一端
Entity Types
independent entity weak or dependent entity associative entity aggragate entity subordinate entity(动物里面有羊和牛,但是如果这个sub很重要就会变成independent entity)
Generalization and Aggregation
Chapter 8 Normalization and Other Data Modeling Methods
Functional dependency
one or more attributes determine the value of another
Normal forms
The hierarchy of normal forms is 5NF(fifth normal forms), 4NF, BCNF(Boyce-Codd), 3NF, 2NF, and 1NF. Thus, 5NF is the outermost doll. DK/NK(domain-key normal form)
1NF
an attribute must have a single value 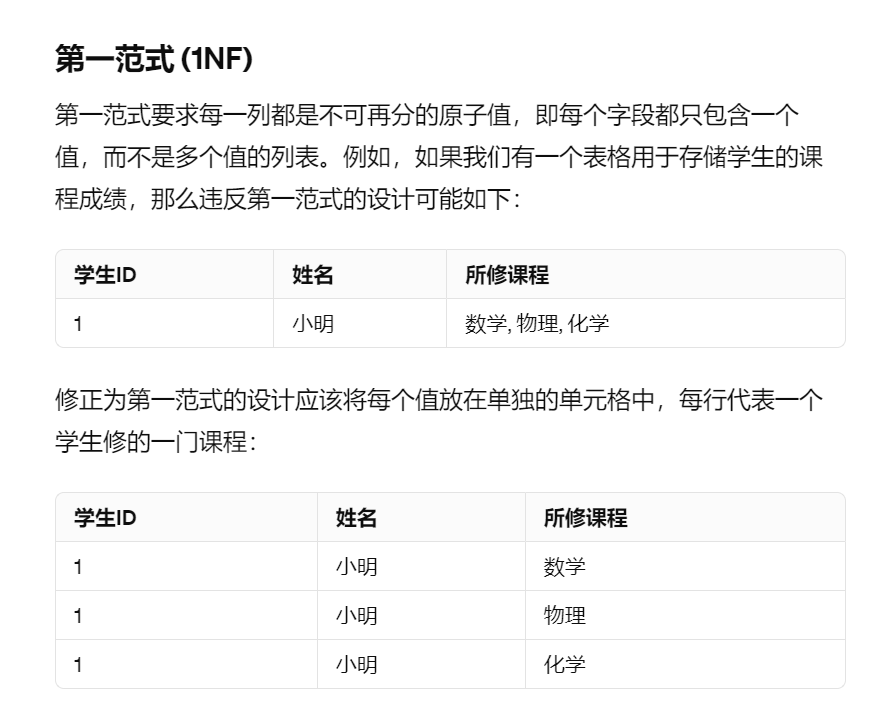
2NF

3NF
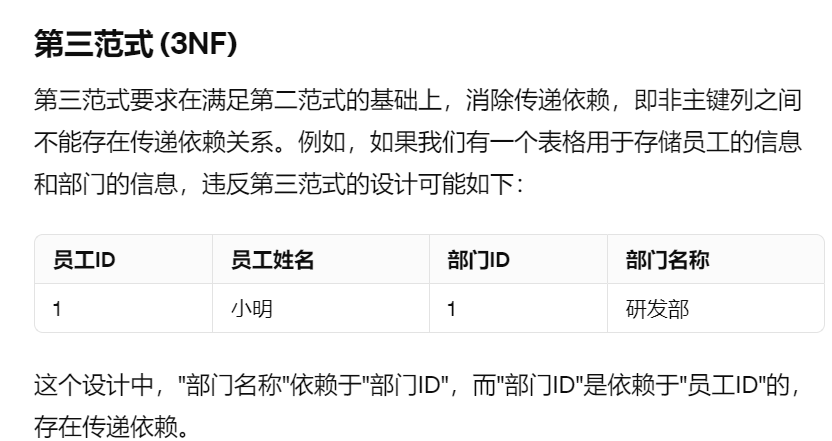
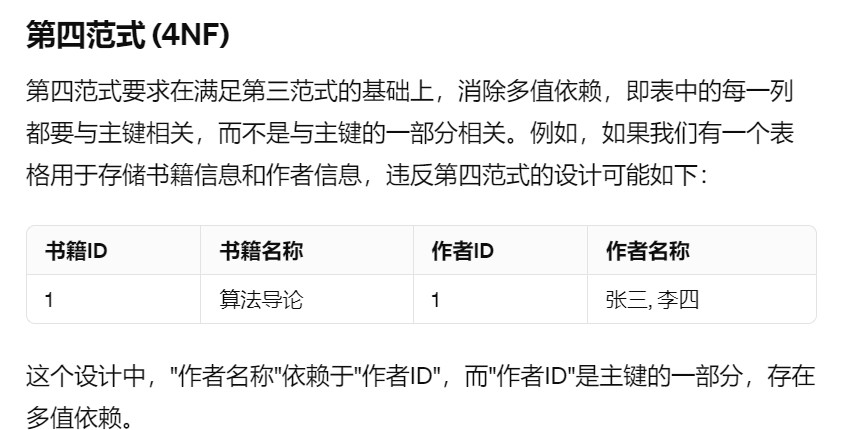
4NF
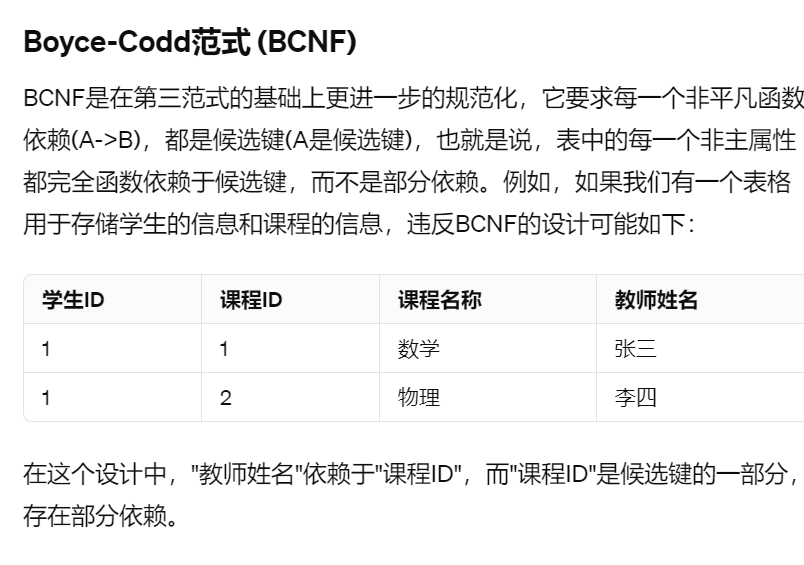
Boyce-Codd
Chapter 9 The Relational Model and Relational Algebra
The relational model data structure
integrity rules
No component of the primary key of a relation may be null. A database must not contain any unmatched foreign key values.
Chapter 10 SQL
structured query language
Data Definition
Key: 它可以是主键和外键的一部分。组合键是同一表的一组有序列。换句话说, lineitem 的主键始终是( lineno , saleno )按顺序组合而成,且无法更改。 Index: An index is an ordered set of pointers to rows of a base table Notation
Constraints 约束条件
Primary key constraint
Foreign key constraint


Unique constraint

Check constraint
Data Types
BOOLEAN Numeric String Datetime Object
Scalar functions(RDBMS manual)
How many days’ sales are stored in the sale table? 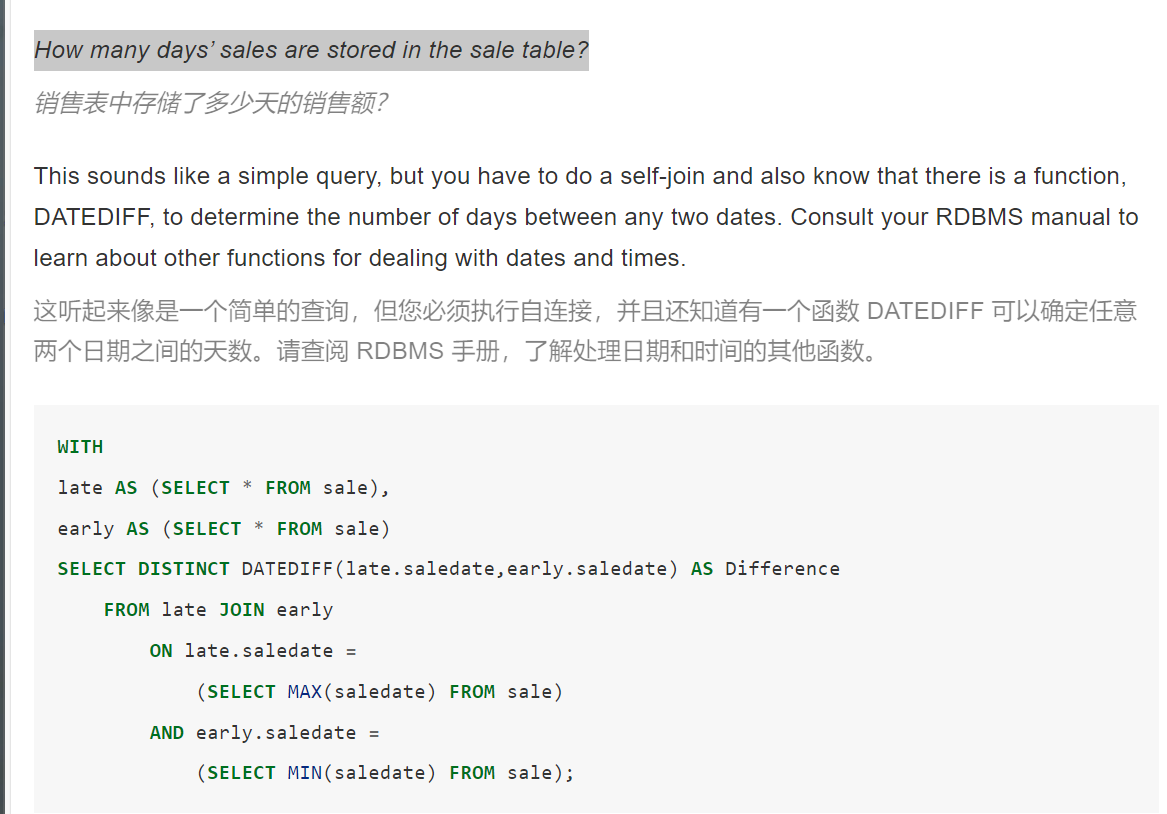
Formatting
SELECT shrfirm, shrprice, shrqty, FORMAT(shrdiv/shrprice*100,2)
AS yield
FROM share;
Table commands
ALTER TABLE base-table ADD column data-type;
DROP TABLE base-table;
CREATE VIEW stklist
AS SELECT stkfirm, stkprice FROM stock;
Index
SELECT
GROUP BY and HAVING
REGEXP
==case==
INSERT
INSERT INTO table [(column [,column] …)]
VALUES (literal [,literal] …);
 就是把download这个表里面选中的那些列,插入到stock这个表里面
就是把download这个表里面选中的那些列,插入到stock这个表里面
UPDATE
UPDATE stock
SET stkqty = stkqty - 200000
WHERE stkcode IN ('FC','BS','NG');
DELETE
DELETE FROM table
[WHERE condition];
Reference SQL playbook
Chapter 11 Spatial and Temporal Data
Spatial data
Managing spatial data
SQL/MM Spatial Spatial Reference Support System
Data model mapping
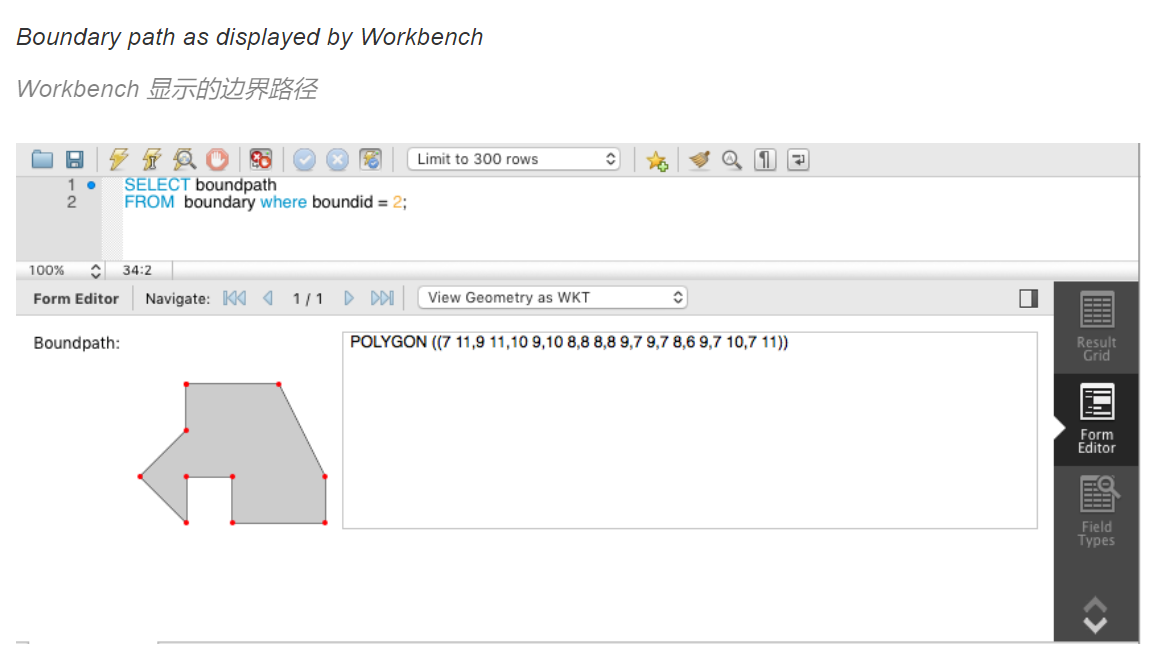
SRID
determine the method of calculating area or distance 比如欧式距离
Geometric functions
ST_X() ST_Area()
Geometry collections
1
MULTIPOINT(9.0 6.1, 8.9 6.0)
2
MULTIPOLYGON(((0 0,10 0,10 10,0 10,0 0)),((5 5,7 5,7 7,5 7, 5 5)))
3
INSERT INTO table VALUES
ST_GeomCollFromText('GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(POINT(1 1),LINESTRING(0 0,1 1,2 2,3 3,4 4))');
R-tree
是B树的扩展
Managing Temporal Data
Transaction time: storing the time of change Valid time: post new prices some time before their effective date Bitemporal data: extra columns to record the upper and lowerr bounds for valid time and transaction time
Times Remembered
Temporal data
Unanchored Anchored: Instant and Interval
文档信息
- 本文作者:Xinyi He
- 本文链接:https://buliangzhang24.github.io/2024/05/01/SQL-Notes-for-Book/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)
